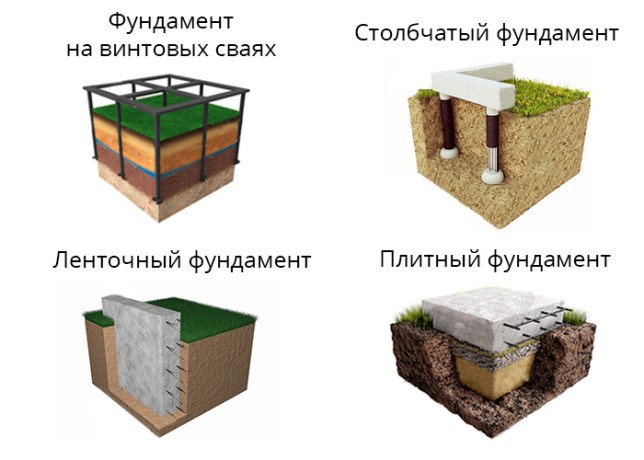
Columnar foundation for a bathhouse
To the question of how to make the foundation for a bathhouse as budget-friendly as possible, there is a simple answer: put it on posts.
You can make a column from a variety of available materials.
- Wooden log or timber.
- Reinforced concrete pile, fence post, stepson for overhead line posts.
- Granite stones.
- Iron ore brick.
- Building blocks.
Bored columns are installed by drilling a hole of the estimated diameter, reinforcing it and filling it with concrete. You can form a well with a pipe, a sheet, or a barrel. Sand is used for backfilling.
It is advisable to use a TISE hand drill. Its peculiarity is that it allows you to make a widening - the sole - at the bottom of the well. This significantly increases the bearing capacity of the foundation.
The depth of the columns is below the freezing point plus 50 cm. The layer of sand and crushed stone for heaving soils is at least 15 cm.
Shallow columnar foundations are made from reinforced concrete rings KS 7.9, with a diameter of 70 or 90 cm. They are dug to a depth of 1 m and filled with sand compacted layer by layer. A reinforced concrete slab of 100 - 120 mm is laid on top. A grillage is arranged along it.
The reliable columnar foundation for the bathhouse is ready.
This type of foundation is most often found in regions where there are certain climatic difficulties. If the soil freezes strongly in winter, or in spring and autumn there is abundant water in the area where the bathhouse is located, a columnar foundation will be the ideal solution.
A columnar foundation made of concrete blocks differs from others in that its main load falls on the pillars dug in at key points. Most often these are corners of the building, places of increased load and areas of intersection of wall ceilings.
The pillars must be spaced evenly so that the load is distributed between them in the same volume. To further reduce pressure, the posts should have an extension at the bottom.
Important! Experts recommend adhering to the standard rule: the distance between adjacent pillars should be a maximum of 3 m.
The top of the pillars remains on the surface. They are fastened together using a grillage, which will perform a function related to the formation of structural stability. Walls made of block material will subsequently rest on this element.
In fact, the pillars are the main fastening, so they must be as strong and reliable as possible. Brick, asbestos-cement pipes, concrete and natural stone are used as materials for pillars. There is no point in installing wooden structures, since they have a limited service life.
Depending on the depth of the pillars, the foundation is of two types:
- Shallow. The level of immersion of the pillars into the ground is small, 40-50 cm.
- With full depth. The most durable type of base. The pillars are located in the ground below the freezing level by 15-20 cm. This ensures the strength of the fastenings and the stability of the structure.
In the case of building a bathhouse, it is recommended to install a columnar foundation only in situations where the structure is erected from lightweight materials and does not have significant dimensions and weight. It should be borne in mind that before starting construction it is better to order a geological analysis of the site. This will help avoid many unexpected situations.
Foundation for a building in a marshy area
Owning a plot of land located in a swampy area should not be upset. Modern construction methods make it possible to build a building even on such terrain. The durability of the structure will depend, first of all, on the type of foundation and materials used. We will consider further what kind of foundation is better in swampy areas.
Soil analysis
What does swampy land represent? This is an area with a porous structure, which is 90% water. The remaining percentage is formed by chaotically located particles of minerals - peat, sand, clay. The unsystematic order of occurrence of rocks does not allow calculating the load on the soil. Soil studies on the site will help identify the following characteristics of the area:
- type of soil mass;
- groundwater volume;
- freezing depth;
- distance of the aquifer from the surface.
The data obtained make it possible to determine the physical properties of the layers, their thickness and depth, and to characterize changes in the soil over the past few years. Based on geological expertise, you can choose which foundation to build in marshy areas.
Characteristics of wetlands from the point of view of foundation construction
Swampy areas are not uncommon in Russia. Large areas may be occupied by swamps, but people are forced to build housing or industrial buildings and structures even in such conditions.
This is especially true for defense needs, as well as for the development of territories in connection with oil and gas production - their deposits are mainly located in swampy areas. Entire cities are built on swamps - an example is the settlements of Western Siberia.
Constructing traditional reinforced concrete foundations for buildings in such places is a big challenge for builders. The fact is that soil saturated with peat does not have sufficient stability, and dense layers of soil are located quite deep.
Even the construction of a small reinforced concrete foundation requires significant excavation work, especially to strengthen the soil - filling Kamaz trucks with sand, installing reinforced formwork, etc. Installing a classic slab or strip reinforced concrete foundation is impossible in some places.
Most buildings and structures in swampy areas are on stilts. However, the installation of reinforced concrete piles is also difficult - their installation requires the use of heavy equipment, which is often impossible to deliver to wetlands.

Foundation in a wetland
Soils in the swamp
A complex of geological surveys costs about 30,000 rubles. Therefore, individual developers often neglect them, independently digging holes in the building spot to a depth of 2 - 2.5 m to study the soil. If you include a pile-screw foundation in the project on marshy soil, you can save this amount:
- It is enough to buy a pile for trial screwing;
- immerse it in 3 - 4 places on the site to get an idea of the depth of the bearing layer.
The method is called test screwing; it must be done manually; when the pile reaches dense soil, this is reflected in a sharp increase in the torque required for further screwing of the pile.
Types of soils in swampy areas.
When choosing a floating slab, it is extremely important in what area the concreting will be done:
- depending on the structure of the upper layers, it will be necessary to replace 60–80 cm (sometimes more) of the peat layer with crushed stone of the 5/20 mm fraction;
- Crushed stone is more expensive than sand, however, after compaction with a vibrating plate, it retains geometry stability when wet.
If you make an underlying layer on top of non-woven material (geotextile), you can prevent mixing of crushed stone with peat. In this case, the slab foundation in the swamp fully lives up to the name floating; it does not settle annually due to the maximum possible support area. Calculation of the bearing capacity taking into account prefabricated loads and the calculated resistance of the soil at the bottom of the swamp is mandatory.
If you need a basement floor, you will have to do a full geological survey, after which the following options are possible:
- the bottom of the swamp at a level within 2 - 2.5 m - a pit below the freezing mark, pumping out water, removing peat, drainage around the perimeter, concreting a strip or making a prefabricated structure from FBS on FL slabs, backfilling with sand, insulating the blind area and the outer surface of the foundation ;
- the bottom of the swamp is deeper than 2.5 m - drainage with vertical drains (steps of 1.5 - 2 m, staggered order) with simultaneous loading of the building area along the perimeter + 2 m of ASG, sand, crushed stone at intervals of 6 - 10 months.
In the latter case, water from the drains is periodically pumped out, the soil is compacted under the weight of the embankment, acquiring the calculated resistance to prefabricated loads from the cottage.
Coarse sand is an excellent basis for any foundation.
The main characteristic for construction is load-bearing capacity, which mainly depends on the moisture content and compaction of the layers. So, the denser it is, the greater the load it can carry without much shrinkage.
But with an increase in moisture in it, it negatively affects the load-bearing capacity (this does not apply to gravelly soil and coarse sand). Sand containing larger particles is better suited than fine or silty sand.
As with any soil, as the depth of the rock increases, the compression resistance also increases accordingly, that is, the deeper the base, the less shrinkage will be.
Measures will be required to protect the base from moisture. Although sand does not retain water, it is impossible to do without waterproofing on sand.
Sandy soil is considered non-heaving, it does not retain moisture, and therefore does not increase in volume when it freezes. So, any type of foundation can be built on such soils. Even if groundwater is close, installing drainage and insulating the base around the perimeter will easily solve the problem.
Shallow tape is the cheapest type. Suitable for a house without a basement. Taking into account shrinkage, it is better to build such a foundation for wooden buildings. Can be mounted from prefabricated elements - for example foundation blocks. A foundation made of blocks stands well on sandy soil.
For buildings with a basement, a recessed tape is suitable. In this case, it is advisable to additionally create a complete drainage system and be sure to waterproof the walls and floor in the basement.
You can use columnar or pile foundations. They are simple, affordable, columnar can be built both for a bathhouse and for a massive structure.
Do not exclude construction on a slab foundation - the most expensive type of foundation.
Before construction, it is advisable to make holes 2 m deep in order to assess the nature of the soil on the site. If there is sandy soil on the site, you can save a lot on the foundation. Usually the groundwater level is low, and there is no need to think about changing the bearing capacity.
Freezing of the soil also does not pose a threat; sand is not a heaving soil. So, don’t worry about the fact that you have sand on your site, this is an excellent option for a foundation.
The question of what kind of foundation to build if the soil consists of coarse sand will not cause any difficulties, since the answer to it is quite obvious - any. Such soil perfectly removes moisture, preventing it from accumulating in the immediate vicinity of the foundation, is resistant to (seasonal) movements, and is not susceptible to frost heaving.
All work on its construction is divided into several stages:
- Cleaning, leveling and marking the site using pegs and rope. Columns are provided not only at the corners of the building and at the intersection of load-bearing walls, but also along external walls, especially those of considerable length.
- Trenches are dug for future posts, in which a gravel backfill is provided, which will eliminate capillary suction of water. A waterproofing layer of roofing material or polymer film should be laid on top.
- The actual erection of the pillars is carried out with the bandaging of all rows, while the number of bricks in one row depends on the desired dimensions, as well as on the thickness of the future walls.
- After this, all pillars are treated with polymer (bitumen) mastic to completely waterproof them, and an additional layer of roll insulation is laid on top.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Features of building a foundation on various types of soil
Use of pile-type foundations
Pile foundations are somewhat inferior in popularity to columnar and strip types of foundations in such a segment as private low-rise construction.
The reason for this is the increased labor intensity of the work, characterized by the involvement of specialized equipment.
As a rule, a pile foundation on heaving soils is used if the depth of soil freezing exceeds one and a half meters. It is also advisable to use a pile foundation when constructing a frame type frame.
If we are talking about private construction, then the depth of the piles is usually used, not exceeding values such as 3-4 m. In our company you can order both the piles and the foundation at average market prices. A very popular solution for the construction of small residential buildings is the use of driven piles from materials such as:
- tree;
- reinforced concrete;
- concrete.
Piles come in the following types:
- reinforced concrete driving units;
- pressed concrete and reinforced concrete;
- screw.
The main thing when constructing a foundation on heaving soil is to ensure high-quality drainage of water. For this, both a drainage system and a device for waterproofing the base along both axes can be used.
Strip foundation for a bath
The most common option, which at relatively low cost ensures maximum stability of the building. Its key advantage is that it can be installed on most soils, including heaving soils.
This base received its name because of its appearance. In essence, this type of foundation for a bathhouse is a strip of concrete with a rectangular or square cross-section. It runs along the entire building and inside it in the area of the partitions. In order for the base to be extremely strong, the width of the tape is at least 10-15 cm greater than that of the wall covering.
This type of base can be monolithic or block. In the first version it is a single structure, in the second it is a prefabricated structure. This means that several concrete blocks are laid on the ground, forming a strip base.
Depending on the depth of burial, a shallow-depth strip foundation for a bathhouse is distinguished and one with full depth. In the first case, the concrete structure is immersed in the ground no more than 30-40 cm. In the second case, the concrete blocks are below the soil freezing level by an average of 15-20 cm.
A simple, traditional and cost-effective type - tape, in various options.
- Monolithic ribbon belt. Reinforced concrete.
- Prefabricated tape. Material – FBS foundation blocks, building concrete.
- Rubble concrete. Rubble stone, concrete.
- Brick. Only baked clay bricks.
- Cellular concrete. Foam blocks of a grade of at least D 1000.
- Pile-tape. Recessed concrete grillage on piles.
The choice is made based on the availability of materials, the costs of their acquisition and delivery.
Monolithic
A concrete reinforced strip foundation for a bathhouse is the most common option. Available everywhere, forgives minor errors in design. Requires quite a lot of materials.
- Sand for pillows, filling sinuses.
- Crushed stone.
- The boards are edged on the inside.
- Bars for posts, struts.
- Reinforcement or mesh.
- Polyethylene film.
- Nails, screws.
- Knitting wire.
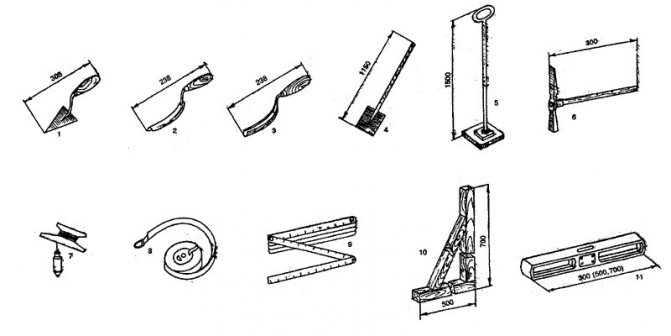
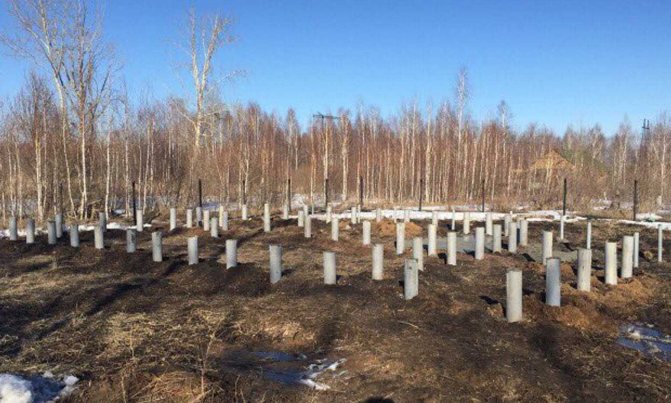
2 and 3 - jointing; 4 - shovel; 5 - rammer; 6 — hammer-pick; 7 - plumb line; 8 — roulette; 9 - meter; 10 - square; 11 — level. Concrete for the foundation of a bathhouse is preferable to factory-made: it is never of poor quality. In its absence, you will have to set up a small concrete-mortar unit. Concrete mixer, warehouse for cement, inert materials, containers for water and concrete.
Do-it-yourself strip foundation for a bathhouse: step-by-step instructions include many rather labor-intensive steps, so if possible, you should use ready-made concrete.
What is soil heaving?
Studying the soil is the primary task before constructing the foundation.
Heaving is nothing more than one of the properties of soil masses, which boils down to an increase in volume during the freezing process.
This feature is explained by the presence of water in the ground. When it turns into ice, the volumetric component increases. Therefore, with a high moisture content in the soil, swelling is inevitable.
Some soils are slightly susceptible to heaving, while others are more susceptible to heaving.
There are also non-heaving soil masses. In this case, the depth of the supporting structure does not matter.
In general, experts recommend deepening the foundations below the freezing level. Then the likelihood of problems during use of the building is significantly reduced.
When the foundation on heaving soil is laid in an area where the ground freezes, with the onset of cold weather the soil will begin to expand. The base will rise slightly upward, despite the significant weight of the building. This can lead to adverse consequences that reduce the durability of the structure.
When laid below the freezing level, the heaving does not disappear anywhere. However, its impact is tangential. The base may also rise, since the soil masses are strongly influenced by non-wall structures from the side sections. Another explanation for the rise is the significant area over which the base connects to the ground.
The described events are observed in wood or frame buildings of small mass. At the same time, the horizontal load indicators of such structures are not very high. It turns out that the load does not have the ability to compensate for heaving forces from the sides.
Most problems associated with foundations on heaving soils occur during thawing.
The soil masses sink, which causes subsidence of the supporting structure. Moreover, the changes are often uneven. The building is distorted, the foundation sooner or later becomes completely unusable.
Pouring a pile-strip foundation is the most critical stage of construction
Housing on sandy land
- the pipes are installed so that their upper part protrudes above the surface, leveled using a level and secured with spacers;
- after the pile is 1/3 filled with concrete, the pipe should be raised, which makes it possible to obtain a thickening at the bottom of the pile;
- after this, the pipe is leveled, pre-prepared fittings (3-4 metal rods with crossbars) are lowered into it, and the pipe is filled with mortar to the end.
Do not forget that the protruding part of the reinforcement must be sufficient so that there are no problems with its subsequent connection with the reinforcement strip of the foundation. One should not ignore the fact that it is better to fill the foundation for a house on sandy soil at a time, or layer by layer, avoiding the formation of vertical seams that reduce the strength of the structure.
Installation of formwork and preparation of mortar
Formwork is a frame made of boards and beams that will become supporting walls for the foundation. The boards must be tightly fitted to each other to avoid leakage of the poured solution. When installing, the formwork must be cleaned and moistened with water. The solution is poured into the formwork in layers of 15 cm, each of which is compacted and leveled. Work on pouring concrete mortar should be carried out in hot sunny weather, avoiding rain and dampness.
When preparing a solution, the quality of the constituent components is very important. Sand and gravel must be dried and free of soil, clay and debris. Don't skimp on the quality of cement! The ratio of components in the solution should be 6 parts gravel to 4 parts sand, the amount of water should not exceed 75% of the mass of cement.
The mixture is prepared in the following sequence:
- take the required amount of sand;
- take the required amount of cement;
- Fill a clean, dry container with the ingredients and mix thoroughly;
- add the required amount of gravel to this mass;
- stir again;
- pour water over the mixture using a watering can or hose with low pressure;
- stir again.
For additional strength, it is recommended to install a frame made of reinforcing bars laid lengthwise and crosswise.
Pile foundation for a bathhouse
Visually, this type of foundation for a bathhouse resembles a columnar foundation. The only exception is that to create a durable structure, metal piles are used, which are placed in the ground at a distance of 3 to 20 m.
After the piles are installed in strategically important places (ceilings, wall structures, building corners and high-pressure zones), they are fastened together with a grillage. This element helps to create a perfectly flat structure on which the base of the bathhouse will subsequently be laid.
Among all the variations of bases, this option is one of the most expensive, and at the same time reliable and durable. Structures of this type can withstand large buildings with a large mass, any type of soil and other adverse influences.
The most popular variations of pile foundations are screw and bored foundations.
The metal pipe is equipped with a special blade, which is responsible for uniformly screwing the mechanism into the ground. In addition, the blade becomes an element of additional fixation after the pile is completely immersed in the soil.
Only metal products that have high protection against corrosion can be used as piles. In addition, it is recommended to cover them with an additional layer of paint with a high level of adhesion. It will create additional anti-corrosion protection and prevent rust.
The only difficulty when installing a foundation of this type will be that in order to immerse it in the soil, it is necessary to adhere to a special technique that will control the depth and level of verticality of immersion.
Important! Under no circumstances should low quality metal be used as piles. Otherwise, it may bend at the stage of screwing in the pile, which will negatively affect the operational parameters of the entire structure.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the beneficial properties of Jasper for baths
To equip the base for a bathhouse of this format, you must perform the following steps:
- Wells are drilled in the ground, the depth of which will correspond to the necessary parameters for driving the pile.

- A metal frame made of reinforcement is installed in the wells, the purpose of which is to fix the hole and prevent it from being subsequently covered with earth.

- Concrete is poured over the reinforcement frame, which, when hardened, forms a solid foundation for the construction of the building.

This option has several disadvantages. One of them is the high cost of the project. In the case of building a bathhouse, laying a bored base will significantly increase the cost of work and materials. In addition, it is extremely difficult to carry out all the actions on your own; you will have to hire professional builders and special equipment.
Ways to counteract heaving
If the foundation is located on problematic soil, a number of measures are taken, among which it makes sense to highlight the following:
- Replacing the soil that is under the foundation with non-heaving soil. Sand and gravel are poured under the supporting structure. Backfilling is also performed with non-heaving materials. But this technique is used when it is necessary to reduce lateral heaving.
- Laying a foundation on heaving soil with wall structures that are smooth. Difficulties caused by heaving are solved by using a waterproofing layer on the side walls. It is this that reduces the adhesion of soil masses and the foundations of the structure.
- Arrangement of the base, the lower part of which is made in the form of an expanded monolith. The option is suitable for many types of support systems. For example, for tape, pillars and piles.
- Laying horizontal thermal insulation of soil masses relative to the perimeter part of the structure. The method is effective only if there is a heating system and a properly insulated basement. The fact is that under a well-heated structure in combination with thermal insulation, heaving does not act so strongly.
It must be remembered that the closer the moisture lies to the surface, the higher the impact of heaving forces. The only exceptions are non-heaving soil masses.
A large amount of moisture in the ground also leads to its erosion. Sometimes liquids contain substances that negatively affect non-concrete structures and reinforcing products. All of these problems are solved by a waterproofing layer.
In the process of drawing up project documentation, seasonal changes in water occurrence should be taken into account. In certain regions, the liquid rises to different heights. The solution to the issue of ground moisture in such situations is the creation of a drainage system. It reduces heaving in the foundation area.
We suggest you read: How to clean a chimney from below
Foundation and bearing capacity of sand
Since the depth of the foundation on sandy soil can be different, including small, it is necessary to carry out work on its high-quality waterproofing and subsequent insulation. This will not only make the future home warmer and more comfortable, but will also maintain the strength of the foundation even with high groundwater.
Foundation protection
Of all the materials presented, extruded polystyrene foam is best suited for foundation insulation - it is suitable for both a shallow foundation for a bathhouse and a massive foundation for a large stone house. Its undoubted advantages include extremely low thermal conductivity, low water absorption, enormous compressive strength, durability and low weight.
Installation is made as easy as possible thanks to the tongue-and-groove system. As practice shows, regardless of which foundation on sandy soil was preferred, its external insulation significantly extends its service life, increases the comfort of living in the house, and reduces heating costs.
Before starting work with insulation, it is necessary to carry out coating waterproofing of the foundation, for which use water-based polymer or bitumen mastic. The use of mastics based on any solvent is not allowed - this may damage the structure of the penoplex. To glue the slabs to the base, it is necessary to use a special glue, which is applied to the slab itself either pointwise (if the foundation is uneven) or over its entire surface (if the base is level).
Slab foundation for a bathhouse
It is used on any soil, including quicksand and peat bogs, with high groundwater levels. Does not shrink and is resistant to frost heaving. But it makes no sense to use this type on strong, stable soils.
It is a reinforced concrete slab on an artificially created foundation. This is a “floating” structure: soil movements during freezing and thawing occur together with the slab.
Pouring the foundation for a bathhouse in the form of a slab allows you to position it above the ground surface, while the slab itself will play the role of a plinth. If you place it below the freezing point, it will be a basement floor; if you sink it into the ground, it will be a semi-basement.
On soft soils, a sand and gravel cushion is required. If groundwater is close to the surface, crushed stone is first poured, then sand in a 10 cm layer. They are compacted and separated - to avoid mixing - with geotextiles.
On large foundations, a 10-centimeter layer of lean concrete is recommended for greater rigidity. The pillow is covered with waterproofing materials in at least 2 layers.
The slab has a thickness of up to 25 cm. Depending on this, a reinforcement frame (d 10-16 mm) is formed so that it is completely hidden in the concrete. The rods are knitted or welded.
After this, the formwork is assembled and poured with M300 concrete with a water permeability of at least W8 and frost resistance F200. The concrete is leveled according to pre-installed beacons: horizontality can only be ensured this way.
The concrete is kept under the film for at least 2 weeks with spillage during the first week.
Recently, in cottage construction, a type such as an insulated Swedish stove has become widespread. Rigid insulation up to 200 mm thick is laid over the sand and gravel base. In places where walls and partitions support, its thickness is up to 100 mm. If you plan to have a heated floor in the bathhouse, then this design will justify itself.
Disadvantages: high cost and labor intensive. Impossibility of pouring on slopes: the slab can slide down along with the bathhouse.
This type of base is better known as monolithic and floating. This is the most expensive foundation option. Its construction requires large financial and time costs, and a huge amount of building materials.
The slab base is a concrete slab, the thickness of which ranges from 10-50 cm. It is installed on a sand and gravel bed. Before starting to form a massive base, it is necessary to level the area as much as possible.
Such a slab is capable of rising and falling simultaneously with the ground, preventing deformation and destruction of the structure located on it. If horizontal displacements of the soil layer are observed in a particular area, the base will require additional stiffeners. In this situation, the structure will be as stable and durable as possible.
Such a foundation is used extremely rarely for the construction of a bathhouse. The main indications for using such a base will be peat soils and quicksand.
The most important advantage of a monolithic slab is its ability to withstand enormous loads. Such a foundation can easily support the weight of a 3-story building. The slab does not react to aggressive chemical components in the soil or the proximity of groundwater. The only caveat is that when forming you need to use sulfate-resistant concrete grades.
Site drainage - luxury or necessity
In the case when a house is being built on fine sandy soil, which tends to retain water, or in an area with a high groundwater level, it is worth considering the presence of a drainage system that will significantly reduce the destructive effect of water on building structures. To create a better foundation, you will not need major financial investments, and all the work can be done with your own hands.
The most convenient and practical is a closed drainage system, where the main role in drainage is performed by various types of pipes - the simplest and most inexpensive option is to use plastic sewer pipes, in which holes must first be drilled. They are laid at a slight slope in a prepared trench dug around the house, the bottom of which is covered with coarse gravel and sand.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with FBS 24.6 foundation blocks, reinforced concrete products, FBS 12 blocks, FBS 9 blocks, block sizes, weight of FBS blocks, weight of blocks
Do-it-yourself foundation for a bathhouse made of tires
Recently, one of the most popular options for arranging a foundation for a bathhouse is the use of car tires. They are laid along the entire perimeter of the building, after which a sand-gravel mixture or crushed stone is poured inside. Next you need to fill the base with concrete, resulting in a fairly strong and reliable foundation.
Tires have gained popularity due to several features:
- Tires are made from a special rubber alloy, which demonstrates resistance to most external factors (except ultraviolet radiation). A tire buried in the ground can last up to 100 years.
- Withstands enormous loads and has sufficient elasticity.
- The product perfectly tolerates high humidity and demonstrates excellent waterproofing functions.
At the same time, the use of tires is inappropriate if the project involves the construction of a massive bathhouse with a large mass. This would be an excellent option as a foundation for small outbuildings. However, in other situations it is better to refuse it.
Conclusion
This material provides overview information that will help you select, calculate and build the required type of foundation on a site, including a foundation for a bathhouse in marshy areas. It is necessary to approach this issue carefully, since such buildings are installed for more than a dozen years. In the video presented in this article you will find additional information on this topic.
Sources
- https://texnotoys.ru/fundament/dlya-bani-na-bolotistoj-mestnosti.html
- https://beton-stroyka.ru/fundament/kak-sdelat-fundament-dlya-bani-svoimi-rukami-na-bolotistom-meste.html
- https://k-dom74.ru/fundament-na-vintovyh-svajah-v-bolotistih-mestnostyah/
- https://GidFundament.ru/vybor/kakoj-luchshe-na-bolotistoj-mestnosti.html
- https://Proekt-sam.ru/fundamenty/fundament-na-bolotistoy-pochve.html
- https://9ban.ru/elementy/fundamyent/628-fundament-pod-banyu
Types of sandy soils
Dusty is the most unfortunate type of foundation, because the bearing capacity of such soil largely depends on moisture. When moistened it resembles clay. The content of particles larger than 0.1 mm is no more than 75%;

Fine - with increasing humidity, as with silty sands, the bearing capacity decreases. When building a foundation, you need to take into account the fact that it is necessary to waterproof the trench with plastic film. The content of particles larger than 0.1 is more than 75%;
Medium-sized and coarse sandy soils contain more than 50% of particles larger than 0.25 mm and 0.5 mm. They have high load-bearing capacity and are an excellent foundation for a house;
Gravelly - contains more than 25% of particles whose size exceeds 2 mm. Such a base will be ideal for the construction of any type of foundation.
Water practically does not linger in sand, which makes it an ideal material for foundations. However, it is worth pointing out some features of this material. Wet sand can compact its structure, which can cause soil displacement.
Therefore, it is recommended to use a sand cushion before laying the foundation. It can be wheels and barrels filled with crushed stone, gravel or the same sand. The sand layer will allow you to quickly get rid of excess water, which is especially important for areas where groundwater is close to the surface.
Foundation for a bathhouse - which one is better?
The answer is obvious. One that suits the soil, climatic conditions and is not burdensome in terms of finances and labor costs. The availability of materials and construction equipment for these works is also important. Main types.
- Tape.
- Slab.
- Columnar.
- Pile.
Each has advantages and disadvantages. Let's look at each of them in detail. General site preparation is set out in SP 31-105-2002.
It is extremely difficult to give an unambiguous answer to the question of which foundation would be the ideal choice when building a bathhouse. It all depends on many factors, including the type of soil and buildings.
The recommendations given by experts, based on the type of planned construction, come down to several rules:
- Log house or wooden beam. Any type of foundation will do, but if there is no soil heaving on the site, it is better to choose a strip or columnar one.

- Frame or panel bath. It is characterized by a small mass, so the foundation does not have to be solid. The simplest option is columnar, but in situations where there is no problem with soil heaving.

- Foam block structure. By analogy with frame and panel buildings.

- Cinder block. It is a heavy building material, so columnar or strip foundations can support it.

- Brick bathhouse. It has a large mass, so the base must be extremely strong. The ideal option is a strip or tile foundation.

The main feature of clay is its ability to absorb and retain water. At the same time, the building material swells greatly and increases in size. After the water dries, the clay returns to its previous volume and cracks violently.
In winter, active swelling is observed in clay soils. This is explained by the fact that water under the influence of sub-zero temperatures turns into ice, which further increases the volume of clay. As a result, the nearby soil under pressure begins to move both vertically and horizontally. All this entails the destruction of the bathhouse.
Since the amount of clay in the soil is uneven, the swelling process also occurs unevenly. Some areas rise much faster than others. This leads to additional problems, since in such a situation the foundation and walls of the bathhouse will be at risk of deformation and partial destruction.
Due to the characteristics of this material, when building a bathhouse on clay soil, it is recommended to remove part of the soil and replace it with a sand-gravel mixture. A strip or monolithic foundation will be laid on top of it.
If the site is located in a swampy area, the ideal solution for building a bathhouse would be a combined or pile foundation. However, before construction operations can begin, it will be necessary to drain the water.
Pumping out the liquid will remove excess moisture, which will make the process of arranging the foundation simpler and faster.
If there is a large difference in elevation on the site, the construction of a bathhouse, like any other building, will be complicated. In order to equip a strong and reliable foundation, it will be necessary to level the construction site as much as possible. Since it is impossible to do this in a number of situations, and in others the operation will be too expensive, the only correct solution is to use a pile foundation.
If there is a difference in height, the piles can be buried at different depths. After laying the grillage on them, the base will become as level as possible. This will make it possible to build a bathhouse on the site.
Briefly about uneven settlement of building foundations
Uneven subsidence of the foundation is death for the entire structure; correcting such things costs a lot of money, especially if the building is large.
As you already know, with the onset of cold weather, heaving masses freeze due to their moisture content. The volume increases, the soil bulges. The layers rise within the limits set by the freezing depth.
Any load-bearing structure located on a plot of land will necessarily undergo uneven shrinkage.
Deformation forces will make their contribution to destructive processes. All this is observed if the perimeter part of the building does not resist heaving.
Why does uneven settlement occur? The reason lies in the uneven influence of heaving forces. The rise and subsequent fall after a certain period of time accumulate.
Cracks form on the surface of the foundation. According to the established rules, they are unacceptable, as they lead to complete destruction of the foundation.
If we take settlement as a basis for the problem, it is necessary to take into account the type of wall structures of the structure being built.
Walls are either light or heavy. Based on this, on heaving soil it is quite possible to erect a building from the following materials without any particular difficulties - wood, foam blocks, concrete, brick. Ultimately, the walls have a direct impact on the laying of the foundation, which must take into account all loads in a comprehensive manner.

After reading the article, you may have the opinion that foundations on heaving soils are very dangerous structures that do not have a long service life. Let's reveal a little secret, although it is not a secret at all. Today, thousands of houses are built on soils with a high moisture content.











