- 6478
- columnar foundation foundation for a bathhouse
You are planning to build a bathhouse. If you are lucky with the soil (dense, not shifting, the groundwater is deep), you can install a columnar foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands: it is cheaper than others, technically simpler and faster to install.
Posts are the best choice on uneven terrain (like piles, but are much cheaper than piles). Good soils include coarse sand, gravel, and loam.
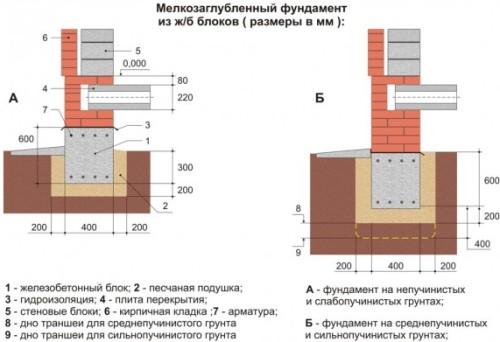
In addition to the soil, the choice of foundation is influenced by the weight of the building: pillars are suitable for a wooden or frame bathhouse; for a heavy brick structure it is better to use a concrete strip. A columnar foundation for a bathhouse made of blocks or bricks should be made with a reinforced concrete grillage.
Selection and technology of building a foundation for a bathhouse
A modern bathhouse is a lightweight structure made of logs or timber that can stand on any type of foundation.
When choosing a foundation, you need to take into account the characteristics of the soil on the site and economic feasibility - extremely reliable foundations made of a monolithic slab or reinforced concrete piles for a small bathhouse with an area of up to 6x6 m will simply be unnecessary. Bathhouse on a strip foundation
In this article we will look at the optimal types of foundations for a bathhouse, give recommendations on their calculation and DIY technology. Strip, columnar, screw and slab foundations, as well as cheap tire foundations, will be examined in detail.
Choosing a foundation for a bath
When choosing which foundation is best for a bathhouse, you need to consider three factors:
- weight and size characteristics of the structure;
- geological conditions on the site - presence of a slope, type of soil and its bearing capacity, freezing depth and groundwater level;
- budget allocated for construction.
In most cases, the best option would be a strip foundation for a bathhouse . The different depths of the strip foundation allow you to build in any soil conditions - on stable soil it is rational to construct a shallow strip (deepened by 30-80 cm), in heaving soil - deep strips (the support base is 20-30 cm below the depth of soil freezing).
However, the arrangement of a buried foundation is accompanied by serious costs for materials, and in order to save money, it is better to give preference to screw or columnar foundations.
The screw foundation for a log bathhouse consists of steel piles tied with a grillage, the blades of which open the surface layer of soil and rest on solid deep soil. The advantages of this option are low cost, quick installation time (installing a foundation for a bathhouse takes 2-3 days) and reliability.
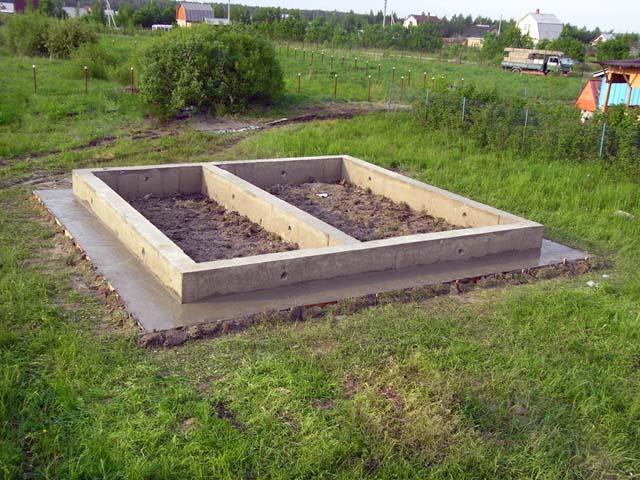

Shallow strip foundation for a bathhouse
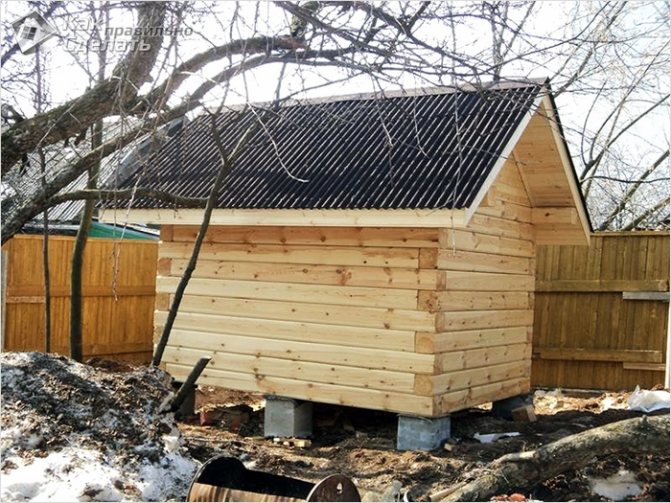
A good analogue for the construction of light buildings (log house, frame panels - area from 3x3 to 6x6 m) is a bathhouse on a columnar foundation. To install a log bathhouse on poles, the soil on the site must not be prone to horizontal shifts, otherwise there is a high risk of the supports overturning. The pillars can be monolithic (concreted asbestos pipes) or prefabricated (from FBS blocks).
In complex soils - mobile, heaving and low-density - a foundation slab is needed. This is a monolithic structure made of reinforced concrete 30-50 cm thick, the dimensions of which correspond to the area of the building. The slab is a reliable and durable foundation for a frame bathhouse or log house, but its cost is higher than other analogues.
A simple foundation for a bathhouse, suitable for light frame buildings measuring 3x3 and 3x4 m - a base made of car tires. It is possible to erect a building on such a foundation in stable soil that is not prone to heaving. A bathhouse without a foundation can only be built on rocky soils.
Collection of characteristics and calculation of the foundation
Before building a foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands, you need to calculate the foundation and find out whether it will withstand the building in specific soil conditions. You need to determine the type of soil on the site (sandy, clayey, sandy loam) and, using standard tables, find out the value of its resistance per 1 cm 2.
Next, you need to calculate the loads that will be transmitted by the foundation to the soil. Load calculations are performed using the following algorithm:
- Calculation of the mass of a building - the weight of the roof, floors and walls is separately calculated and summed up by multiplying their area by the specific weight of the building material (tabular data).
- Calculation of snow loads - multiply the roof area by the weight of m 2 of snow cover in your region.
- Calculation of operational loads (furniture, stove, wall cladding) - multiply the area of the basement floor by the average load of 100 kg.
- Calculation of total loads - we summarize the obtained data and add a safety margin by multiplying the amount by 1.2.
It remains to determine the supporting area of the foundation, multiplying its perimeter by its width, and calculate the load per 1 cm 2 of soil.
For example: the standard width of the tape for log walls is 30 cm, for a bathhouse with an area of 6 × 6 m (perimeter 24 m) its supporting area will be 240 * 30 = 7200 cm 2, for a 3 × 3 building - 3600 cm 2, for 3x4 bath - 4200 cm 2, and so on. Now you need to divide the total loads by the supporting area and compare the resulting value with the resistance of 1 cm 2 of soil; if the result exceeds the bearing capacity, you will need to increase the area where the foundation rests on the ground by adding the width of the tape or the diameter of the pillars.
What materials can a columnar foundation be made from?
To construct pillars, you can use any materials with sufficient load-bearing capacity. Most often used:
- logs treated with antiseptic. They are usually fired before installation. This is a cheap and easy-to-make foundation, but with very low durability, no more than 5 years;
- reinforced concrete beams;
- hollow metal or asbestos cement pipes. After installation, they are filled with concrete;
- brick, stone;
- concrete, rubble concrete blocks.
The pillars are placed at the corners of the house, at the intersection points of the walls, in places of increased loads and are tied with a grillage so that they do not move apart during horizontal movements, and also so that the weight of the structure is distributed evenly across all supports. Depending on the bathhouse material, monolithic reinforced concrete, logs or timber, and metal profile pipes are suitable for constructing a grillage.
Extensions (porch, etc.) are separated from the main structure by an expansion joint, because they have a different weight and draft.
The recommended cross-section of a brick pillar is 38 by 38 centimeters or 50 by 50, a rubble concrete pillar is 60 by 60. The spacing between pillars is from one and a half to 2.5 meters. At a step of more than two meters, additional ones with a smaller thickness are placed between the main pillars. For example, if the main column is 38 by 38, the additional one is made 38 by 25. The immersion depth of the sole is from 0.5 to 0.7 meters.
Procedure:
- Pour 15 cm of coarse sand into the bottom of the hole.
- Sprinkle with water to seal.
- Lay bricks or blocks on cement mortar.
- After laying, sand the seams and plaster the surface of the blocks.
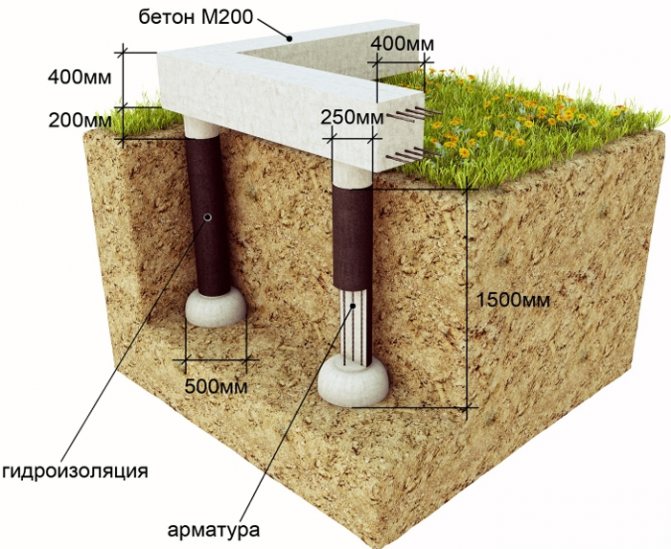
Asbestos cement pipes
For the pillars, pipes with a cross section of 20 centimeters are used. The width of the holes for them is 25 cm, the depth is the level of soil freezing plus 40 cm. The spacing between the pillars is one and a half meters. They are installed around the perimeter of the bathhouse and (with the same step) under load-bearing internal walls. Procedure:
- Dig holes (or drill with a garden drill).
- Pour sand onto the bottom, layer thickness - 20 centimeters. Sprinkle with water and compact.
- The pipe section should be 40 cm larger than the depth of the pit. You can cut with a grinder with a concrete disc.
- Before installation, wrap the pipe with roofing felt.
- Install in the hole.
- Fill the lower part of the hole (40 cm) with crushed stone.
- Pour concrete into the lower half meter of the pipe.
- Lift the pipe and allow the concrete to spread along the bottom. Lower the pipe and press it into the concrete. Align vertically.
- Fill the hole with fine gravel.
- Place several reinforcing bars in the pipe and fill it with concrete to the top. Compact and release the air with a piece of reinforcement.
Before you start, you need to choose the most optimal option for creating the base of a bathhouse made of timber. For the construction of pillars the following is used:
- Stone. This material is strong enough to support a two-story structure, so when using it you don’t have to worry about the reliability of the base for a timber bathhouse. But it is worth remembering that such material has a high cost.
- Brick. This material is more accessible. But not every type of brick is suitable for creating a columnar foundation.
- Concrete blocks. The size of such products allows the foundation to be installed in a short period of time.
- Asbestos cement pipes. Such products are installed in pre-created recesses and filled with concrete mortar.
Wood is usually not used when creating a foundation for a timber bathhouse, since in many buildings the drain is installed directly under the building, which increases the risk of destruction of the foundation due to constant exposure to moisture. When creating a columnar foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands, it is worth remembering that before starting work you need to accurately calculate the load on the foundation.
Do-it-yourself foundation construction technology
When considering the question of how to make a foundation for a bathhouse, we focus on the fact that the floor slab of the bathhouse must be equipped with a drain, which is installed at the stage of pouring the foundation.
In the wall of the strip foundation it is necessary to provide a hole for the drainage pipe, and the floor of the bathhouse itself - a concrete screed or a joist floor, should be made with a slope towards the central part, in which a drain hole covered with a metal mesh is placed. The water is discharged through a pipe into a storage well located outside the bathhouse at a distance of 2-3 meters.
Strip foundation
A shallow strip foundation is the optimal solution for building a log bathhouse with an area of 4×6 to 6×6 m. The supporting part of the MLF is placed at a depth of 30-50 cm, and 20-30 cm of strip is also formed above the ground level, which is used as a base.
Let's look at how to properly pour the foundation for a bathhouse:
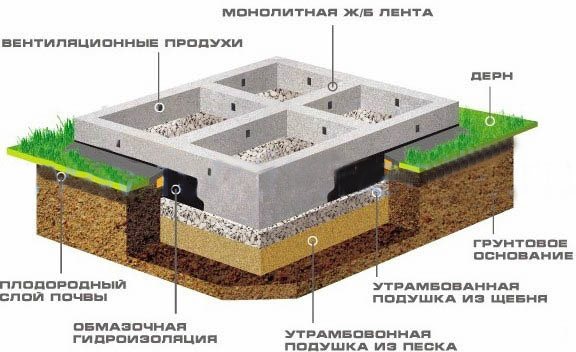
Strip foundation diagram
- The foundation is marked - its design contours are transferred to the site using reinforcement pegs and twine.
- Using shovels, a trench is dug to the depth of the tape plus 20 cm under the compacting bedding;
- A layer of sand 10 cm thick is formed at the bottom of the trench, and on top of it is a layer of crushed stone of similar thickness. The bedding is carefully compacted by compaction.
- Outside the trench, formwork is installed from boards 1-2 cm thick, which will form the ground part of the tape. The structure is strengthened with stakes and spacers. The trench and formwork walls are covered with waterproofing material.
- The foundation is reinforced with a double-circuit frame made of reinforcement with a diameter of 12-16 mm. The upper and lower belts of the foundation are connected by vertical jumpers in increments of 40 cm. Proper reinforcement of the corners of the tape - the frame should not be connected by a cross joint, but by rods curved at right angles.
- After the reinforcement is completed and the assembled frame is installed in the formwork, the shallow foundation is concreted with concrete grade M200-M300.
The formwork is dismantled 2 weeks after pouring, after which the floor can be laid out and the walls of the log house can be raised. The floor will need to be insulated to prevent heat loss from the bath through the ceiling. If you are making a joist floor, insulation (mineral wool, polystyrene foam or EPS) is laid between the joists and covered with facing boards.
Waterproofing the insulation is important - it needs to be covered on both sides with a PVC membrane that prevents the material from rotting under the influence of high air humidity. Waterproofing is also laid along the upper contour of the tape on which the basement of the bathhouse is placed.
Device
The foundation is created not only taking into account the type of soil on which the bathhouse will be built, but also the materials of the future foundation. Soil information should be recorded from previous construction work on the site. If for some reason it is missing, then geological surveys must be carried out independently. It is important to understand that a high-quality foundation cannot be built on unexplored soil.
Geological exploration is carried out by special organizations: a drilling machine makes holes from which soil samples are taken. In a special laboratory, the soil is examined - its chemical composition and physical and mechanical properties are determined. Ground excavations are made along the entire perimeter, below communications and at different depths, in order to obtain a complete geological map of the area. This process requires a lot of time and money, but there are more economical options.
The basic properties of the soil can be determined independently. To do this, you need to dig several wells, trying to make the well as deep as possible. The ideal hole would be one that reaches the freezing depth of the soil. Craftsmen recommend using a garden auger as a tool. Using dug wells, the thickness of the fertile soil layer, the boundary of groundwater and the composition of the soil are determined.
The foundation must pass through the soft fertile layer and rest on a harder structure. If the soil in the area is heaving (mounds and cracks are visible on the surface), then the foundation must be lowered to the level of soil freezing. The soil around the supports is covered with a mixture of sand and gravel so that when groundwater freezes it does not lead to displacement of the base. A shallow foundation is laid only under standard conditions.
If there are sharp changes in elevation at the construction site, then a pile-screw foundation is suitable for such an area.
Piles are not recommended to be installed in areas with high groundwater levels. The interaction of supports with water will lead to rapid corrosion and subsidence of the foundation. Before installation, the piles must be treated with a special solution that protects the structure from moisture.
For moving soils, a pile-grillage foundation is suitable. This type is well suited as a base for brick and block structures. Piles support the structure during landslides and shifts, providing stability to the foundation. Grillage - a tape connecting the supports, designed to evenly distribute the load. It is made of metal, wood or reinforced concrete.
The columnar foundation is intended for regions with deep soil freezing. This type of foundation is also used in the construction of buildings in waterlogged areas and marshy soils. In areas subject to soil movement, a columnar foundation is not installed. It does not tolerate shifts and landslides well.
The most reliable type of foundation is monolithic. A concrete slab can withstand any difficult conditions, maintaining integrity and stability. The solid base evenly distributes the load on the ground, preventing settlement. The main disadvantage of this base is the high price.
Among the materials for building a foundation for a bathhouse, preference should be given to natural materials. Wood is better suited for a pile foundation. Slab and strip foundations are usually built from heavy materials - stone and concrete.
The strip structure is the most reliable type of foundation. Craftsmen advise choosing this option for those who want to do the work with their own hands. This type of foundation is suitable for a building of any size. It is a ribbon of concrete or brick that rests on the ground below the groundwater level. No more than twenty centimeters of the base is left on the surface.
A strip foundation is suitable for any structure, but experts identify several of the most optimal cases for installing such a foundation:
- The basement floor is used for installing a pump and communications, and storing household items. The walls of the basement must be protected from the influence of variable water levels, wind and low temperatures.
- The bathhouse building is heavy and reaches impressive dimensions. The strip foundation absorbs the load from the structure well and transfers it to the ground. This type of foundation is suitable for brick buildings.
There are several methods for assembling a strip foundation. Each method has a number of pros and cons. Brick strip masonry is installed on dry sandy soils. In case of high groundwater levels, the structure is placed on a brick-crushed stone cushion, reinforced and filled with concrete screed. The brick strip foundation is lightweight and easy to install.
It is important to understand that to create such a base you need to choose the right material.
In what cases can it be used?

Therefore, it is most advisable to build wooden houses on it , since they are resistant to tensile loads.
The soil on which the foundation is planned to be built must also meet certain requirements:
- It is better not to use a rubble foundation for a house on soils that are too heaving . If such a decision is nevertheless made, then the soil must be well compacted before laying the sand cushion.
- The soil should not sag , since the rubble foundation has a large mass, so it should not be erected on peat, sandy and clayey areas.
- For the construction of such a foundation, soil with any moisture content is suitable , and waterproofing is created only at the level of the grillage. But if the soil is too watery or when building a house with a basement, you will need to build a drainage system.
Other types of columnar foundations presented on our website: reinforced concrete (made of blocks or prefabricated), bored (with a grillage), brick, wood.
Preparation and calculation
First, you need to draw a diagram of the site in accordance with the scale, designate the area for the installation of a bathhouse and conduct communications to it. The location of the building largely depends on the drainage device. When connecting the water drainage to the central sewer system, the bathhouse can be located anywhere in the summer cottage. If the drain is separate, then it is better to place the building away from bodies of water.
The bathhouse area must be fenced off from outsiders - a fence is needed on the site. The building can be surrounded by hedges. All additional plantings or extensions are also marked on the site plan.
The work begins with cutting off the top layer of soil. Next, the area needs to be leveled. This can be done using special equipment. Changes in height should be avoided - this will complicate the marking and make it impossible to lay the foundation evenly. The marking is made based on the design on paper, so the further arrangement of the base depends on the accuracy of the terrain image.
Columnar foundation for a bathhouse
The construction of any building or structure begins with the arrangement of the foundation. The same applies to the bathhouse. If your site is located on rocky terrain or the area is often flooded, then a columnar foundation for a bathhouse is exactly what you need to complete the first stage towards the construction of this building. In our article we will tell you how to build such a base, what options it may have, and what materials you will need for the work. In addition, a step-by-step guide to performing the work will help you make your own foundation as correctly and quickly as possible.
Peculiarities
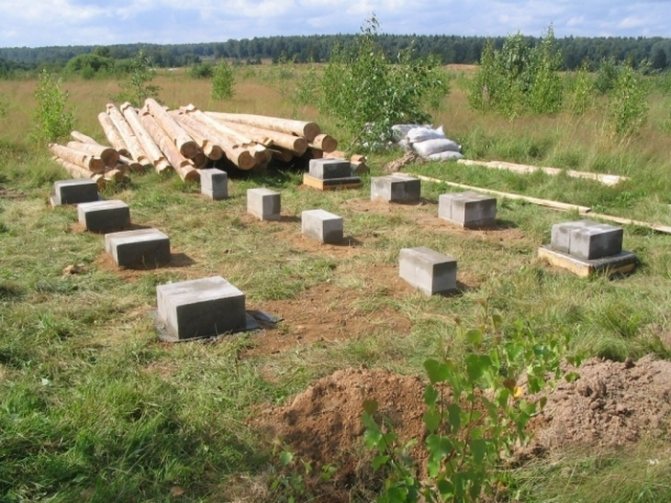

First, let's figure out what this type of foundation is. Externally, the entire structure looks like a grid of columns, which are located with a certain step under the load-bearing walls and nodal points of the future structure.
Important: columns are installed along load-bearing walls, at the places where they intersect and where columns are located, as well as under internal partitions and heavy structures, such as a stove or fireplace.
The optimal pitch of the posts is 150-250 cm. In order for the structure to acquire additional rigidity, the posts are connected with a grillage. It will not only serve as a connector between the pillars, but will also serve as a support for the walls and the basis for arranging the base.
The choice of material for making posts depends on the type of soil and the weight of the future structure. So, the columns can be brick, concrete, reinforced concrete, rubble concrete. There are also steel, stone, wooden poles or products made from asbestos-cement pipes.
Advantages and disadvantages

A columnar foundation has several advantages over other types of foundations:
- The cost of installation of such a foundation and physical costs are several times less than when constructing a strip foundation.
- Such bases are practically not susceptible to heaving under conditions of severe soil freezing.
- The draft of such a base is significantly lower than that of a strip structure.
- If, according to calculations, the width of the strip base is more than 1.5 m, then it is much easier and cheaper to make a columnar version of the foundation.
The only drawback of such a base is associated with its low load-bearing capacity. That is, it can be constructed for buildings with light weight, which do not significantly load the foundations. For example, such a foundation can be made for wooden and frame houses, but it is not suitable for brick, concrete and stone buildings. That is why a columnar foundation is an ideal foundation for a wooden bathhouse.
Which foundation is preferable?
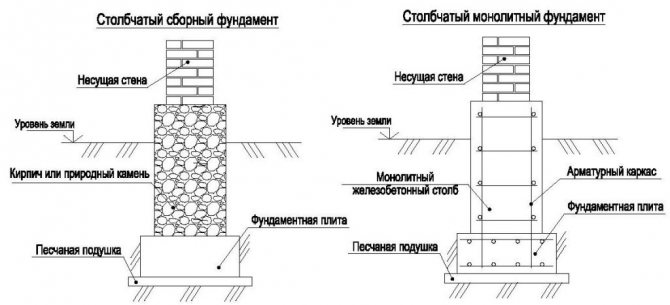
Scheme of laying a columnar foundation.
For a wooden bathhouse, the most suitable option would be a columnar foundation, which will provide significant savings in building materials.
When building cobblestone, frame and log baths, when there is no need for special jumpers between the pillars, its advantages are obvious. However, such a foundation is not applicable when constructing a bathhouse with walls made of heavy structures on weak-bearing soils.
Strip foundations are used both in the construction of heavy stone walls and for chopped wooden ones. This type of foundation is distinguished by its simplicity of technology, but it is more massive, labor-intensive and costly in terms of the amount of materials. But it also has an undoubted advantage: there is no need to lay the foundation to great depth.
Design nuances

All columnar foundations can be divided into two types:
- Recessed. The bottom of such foundations should be 0.5-1 m below the freezing point of the ground in the region. This option is suitable for clay soils and can also be used in conditions of high groundwater levels.
- Shallow foundations sink 0.4-0.7 m into the ground. They are suitable for soils with high bearing capacity.
Despite the fact that a wooden bathhouse is a lightweight structure, on heaving soils it is better to use a buried columnar foundation. The thing is that in the case of using a shallow foundation with a small weight of the entire structure, heaving forces will affect the foundation more strongly than the weight of the building. This can lead to deformation of the structure and the formation of cracks.
Depending on the material used, the optimal cross-section values for the columns are as follows:
- stone pillars can be made with a cross section of at least 50-60 cm;
- brick columns are laid out with a section of 380x380 mm;
- monolithic structures are poured with dimensions of 400x400 mm;
- wooden poles are usually made from logs with a diameter of at least 0.2 m.
To correctly determine the dimensions of the pillars, it is necessary to perform an engineering calculation, which takes into account the following indicators:
- the weight of the entire structure;
- geological conditions and soil composition;
- soil freezing depth (the bottom of the pillars should be below this mark);
- height of groundwater and seasonal changes in this level. It is best that the pillars do not reach the groundwater level.
Conventional pile and support-column foundations
A simple pile type of foundation looks like several piles that stand in those places where the greatest load occurs (in the corners of the house, under load-bearing beams, etc.).
Columnar-type foundations are built for structures that do not have basements or cellars. This type of base is especially often made for wooden buildings made of timber. The supporting beams for such a foundation are laid on supports - piles or pillars.
The structure of such a base can be made of wood or stone. To build such a foundation for a house, use the butt part of a tree pillar (the part next to the root). Typically, the diameter of the butt part varies from 18 to 25 cm.
Photo:
For verandas and houses made of timber, a wooden foundation is most often used.
In addition to the usual columnar foundation, there are several other types of foundations for a house. Among them, a monolithic pile base is distinguished.
Externally, it is a concrete base without seams. It is very durable, and this is its main advantage.
The second type is a prefabricated columnar base. It is built from stones, bricks and reinforced concrete blocks. The main advantage is that construction proceeds very quickly. But due to the not very reliable seams, this design is not particularly durable.
Columnar foundations differ not only in the principle of construction, but also in their depth. There is a shallow columnar foundation and a recessed one.
The first type involves deepening the supports from 40 to 70 cm. Typically, a shallow columnar foundation is made in an area with rocky or sandy soil.
Photo:
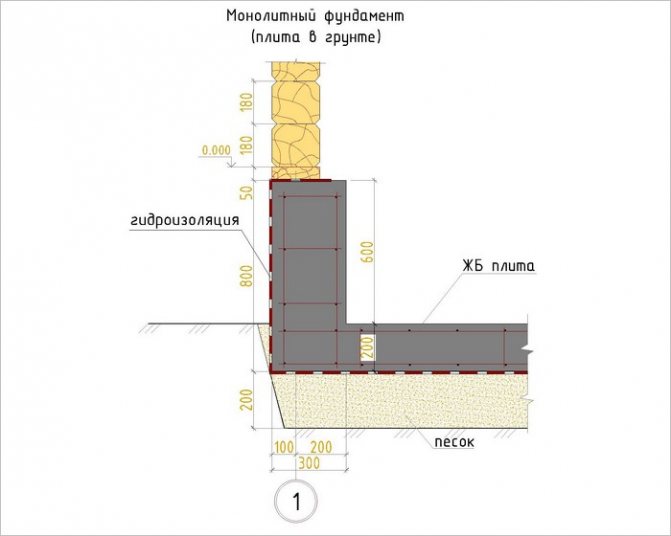
At a recessed base, the supports go to a depth of 0.5 to 1 m, i.e. below the soil freezing zone. Often this type of foundation is made on clay soil, which has a lot of water.
There are other types of pile foundations, which will be discussed in more detail below.
The general construction technology is basically the same, as is the construction of a columnar foundation of any type.
One of the most popular types is the support-column foundation. Most often it is used for the construction of wooden houses from timber.
Its cost is quite low, so the support-column foundation is popular. Often, a support-column foundation is used to build a bathhouse or veranda.
The supports are installed at the corners of the building and under the walls into which windows and doors are built. The distance between the base pillars should be from 1.5 to 2 m.
If a bathhouse is being built, then a cushion of sand is formed, and then a support-column foundation is built directly on it.
Photo:
The supports are dug into the ground, and then the next ones are attached to them to the desired height. The same method is used to construct wooden buildings from timber.
A columnar foundation is not suitable for a brick house. You can try to make such a foundation for a house from foam blocks, but you need to carefully calculate the columnar foundation so that the piles can withstand the load of the structure.
If the construction of a house is carried out from foam blocks, then everything needs to be calculated correctly so that the construction goes faster.
Sometimes a pile foundation is built from plastic pipes. It is usually made for external sewerage. Such a foundation is not suitable for a veranda or bathhouse.
Even though the supports are made of plastic pipes, they can last about 50 years.
In addition, they withstand frost well, and the base made of plastic pipes is quite strong, but at the same time light. The cost of plastic pipes can be different - gray ones are cheaper, orange ones are more expensive.
Video:
Options for columnar foundations for a bathhouse
For such a small structure as a bathhouse, you can use several options for constructing a columnar base:
- support-columnar base made of blocks;
- columnar variety with grillage;
- pipe base;
- bored foundation.
Let's consider each of the listed options in more detail.
Support-column base made of blocks
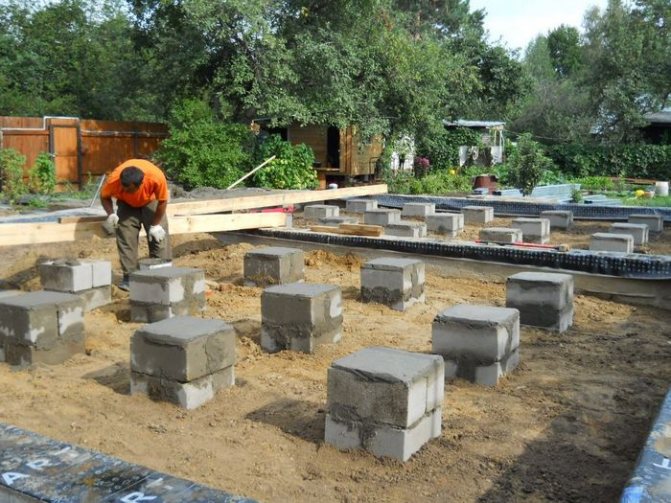

This is the simplest and most affordable option, which is made from ready-made reinforced concrete blocks measuring 0.4x0.2x0.2 m. Based on these standard sizes, you will need 4 blocks for one support.
Such posts are installed at the corners of the building. They are also installed at intersections of structures and under heavy walls. If a stove is built in the bathhouse, then a foundation must also be made under it.
Important: the optimal column spacing is one and a half to two meters.
The work is carried out in the following sequence:
- After laying out the terrain in the right places, they dig holes of the required depth for the pillars.
- Sand is poured into the bottom of each hole, moistened with water and compacted.
- After this, you can begin laying the blocks. The elements are connected to each other using a viscous cement mortar.
- Be sure to waterproof the pillars around the perimeter. You can use roofing material for this.
- After the columns are erected, wooden beams are laid to connect the entire structure. Before laying them, the pillars are covered with two layers of roofing material to insulate the first crown or connecting beam from moisture.
- Before laying the first row of bathhouse logs, the wooden beams must be covered with waterproofing so that moisture from the base is not transferred to the walls.
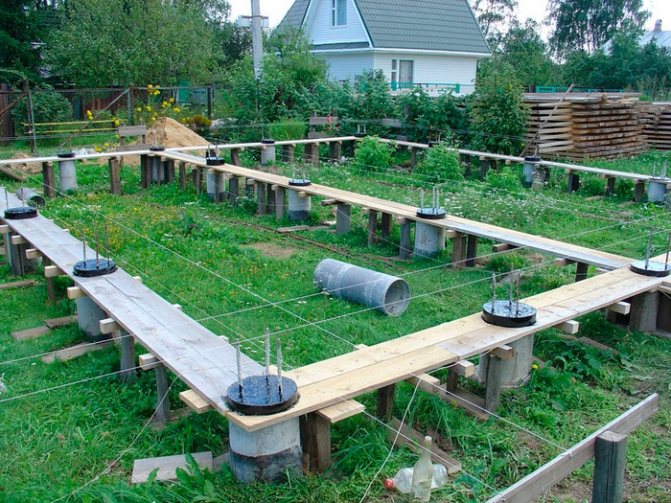
Columnar base with grillage
Thanks to the grillage, the entire base structure will be combined into a single structure, which will make it even stronger. The above-ground part of the bathhouse is installed on the grillage. It is made of beams that are laid on poles and attached to them. This option is more suitable for baths made of piece materials - foam blocks, bricks. When making a wooden structure from a log or timber, the grillage functions are assigned to the first crown or row.
The grillage can be used with different types of columnar bases. At the same time, it can be high and low:
- a low grillage is located below the earth's surface;
- a high grillage is installed on top of the tables.
Important: to construct a grillage, you can use reinforced concrete beams, rolled profiles, metal structures and wooden beams.
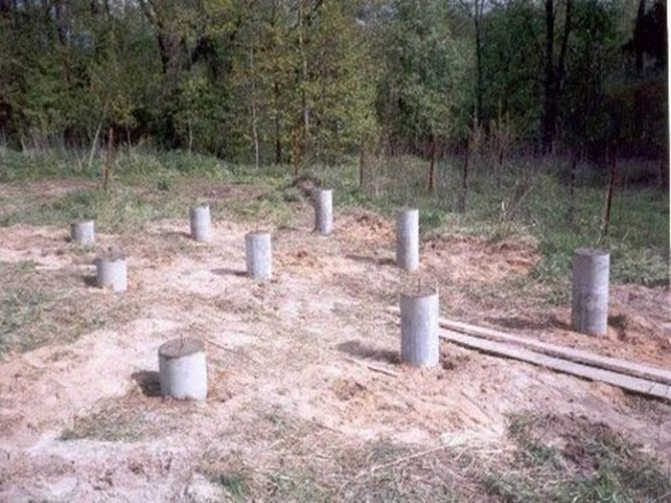
Pipe base

To make the pillars, you can use steel or asbestos-cement pipes of a suitable diameter (usually 20 cm is enough). These pipes will serve as a column and permanent formwork at the same time.
For greater strength, a reinforcement cage is installed inside the hollow pipe and filled with concrete grade of at least 200 (without additives). Installation work is carried out in the following sequence:
- After laying out and digging holes, hollow pipes are installed. The pipes are leveled in a strictly vertical position and fixed.
- A reinforcement frame is placed inside each pipe.
- Then the pipe is filled 1/3 with concrete. After vibropressing, concrete is poured into the rest of the pipe.
Important: instead of special vibropressing, you can use a regular metal pin. They should pierce the solution after pouring, thereby getting rid of air bubbles/
- Then you can fill and compact the soil in the hole around the pipe.
Bored foundation
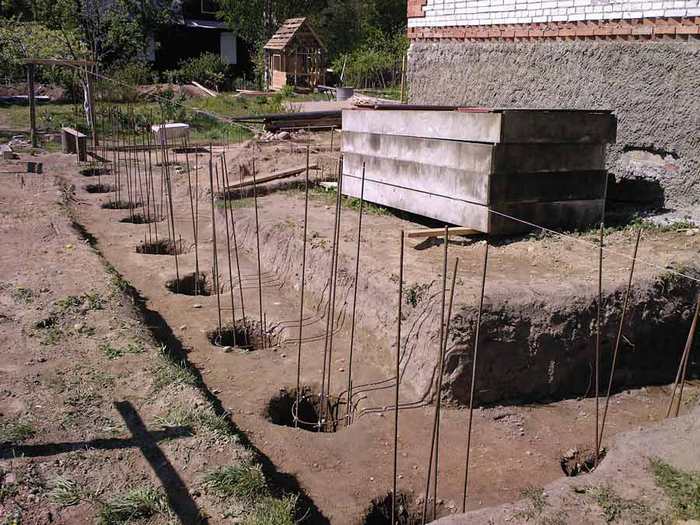

A bored foundation is a cross between a pile and columnar foundation. The essence of the method is as follows: using a drill, a well is drilled into which concrete is then poured. The main advantage of such a foundation is its high load-bearing capacity. It can withstand not only a wooden bathhouse, but also a more permanent structure. The only drawback is the high price and complexity of the work.
The sequence of work is as follows:
- After staking out the terrain, wells are drilled in the right places. The optimal well diameter is 30 cm. And the penetration depth should be 15-20 cm below the freezing mark.
- To improve the performance characteristics, the well walls are treated with a special solution.
- A reinforcement frame made of interconnected reinforcement bars is laid inside the penetration.
- After this, you can pour concrete in several stages, followed by compacting each layer.
- All subsequent construction work on the construction of the bathhouse can be carried out after 28 days (the period for complete hardening of the concrete).
Columnar foundation - how is it presented?
Externally, it looks like several rows of load-bearing pillars located relative to the load-bearing walls. That is, in places with significant load. In principle, this is typical for all types of foundations. In addition to load-bearing walls, pillars are placed at the intersection of external and internal walls. The foundation for the stove, based on pillars, is also prepared according to its size and schematic location. If according to the project a heater will be used for heating.
Over many years of practice, builders have determined the optimal distance between two supports to be 1.5–2.5 meters. To make the structure monolithic, and in order to strengthen the overall frame, for the purpose of subsequent installation of the basement row, above the ground, the supports are connected to each other with a grillage.
The most reliable option for columnar support is reinforced concrete pillars. They are durable and can withstand almost any weight of the structure. But given the relatively light weight of baths, even brick ones, the use of rubble concrete, stone, brick, steel and asbestos-cement pipes is allowed. These materials allow you to save on work. But before choosing them instead of reinforced concrete supports, the soil at the construction site is carefully checked for the presence of groundwater.