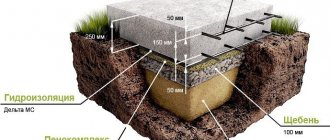
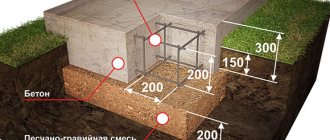
Strip foundation
Foundation depth
In individual construction, the start of general construction work is preceded by the preparation of a project. Thus, in particular, the configuration of the foundation for the building is determined and its dimensions and characteristics are calculated.
The width and length of the foundation, the area of its support depends on the weight of the house structure and the characteristics of the soil on the site.
The depth of the foundation also depends on the characteristics of the soil. This is a fairly important value, because it determines not only and not so much the volume of excavation work when creating formwork for concrete casting of the foundation, not only the costs of purchasing building materials, but also how your foundation will behave during the entire period of operation of your house.
In most parts of our country, cold weather sets in in winter and the ground freezes. The moisture contained in the soil expands and the soil begins to “heave”, that is, to increase its volume, pushing the building structure immersed in it to the surface. This can cause damage to the foundation and structure.
The main regulatory document describing the depth of foundations during construction is the SNiP 2.02.01–83 standard; we will try to present its ideas in an accessible form.
What determines the depth of the foundation?
When determining the optimal foundation depth, the following are usually taken into account:
- Type of soil at the construction site.
- The depth of its freezing.
- Depth of groundwater.
- The number of floors of the building and the density of the main building materials, that is, those factors on which the weight of the house will depend.
- The class of the structure, that is, its expected durability. In private construction it is not taken into account.
Let's look at the first three points in more detail.
What is considered a foundation by law?
Since August 2020, construction permits are not issued, but it is necessary to obtain a notification established by Article 51.1 (not 51) of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation
Quote:
Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 51.1. Notification of the planned construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project or garden house
(introduced by Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 N 340-FZ)
1. For the purpose of construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project or garden house, the developer submits a paper copy through a personal appeal to the federal executive body authorized to issue construction permits, the executive body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or a local government body, including through a multifunctional the center, or sends to the specified authorities by mail with return receipt or a single portal of state and municipal services a notice of the planned construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project or garden house (hereinafter also referred to as the notice of planned construction), containing the following information:
1) last name, first name, patronymic (if any), place of residence of the developer, details of an identity document (for an individual);
2) the name and location of the developer (for a legal entity), as well as the state registration number of the entry on the state registration of a legal entity in the unified state register of legal entities and the taxpayer identification number, except if the applicant is a foreign legal entity;
3) cadastral number of the land plot (if available), address or description of the location of the land plot;
4) information about the developer’s right to the land plot, as well as information about the existence of rights of other persons to the land plot (if there are such persons);
5) information about the type of permitted use of the land plot and the capital construction project (individual housing construction project or garden house);
6) information about the planned parameters of an individual housing construction project or garden house, for the purpose of construction or reconstruction of which a notice of planned construction was submitted, including setbacks from the boundaries of the land plot;
7) information that the individual housing construction project or garden house is not intended to be divided into independent real estate objects;
 postal address and (or) email address for contacting the developer;
postal address and (or) email address for contacting the developer;
9) the method of sending to the developer the notifications provided for in paragraph 2 of part 7 and paragraph 3 of part 8 of this article.
Having ownership of a plot is no exception.
Types of soils
The type and structure of the soil determine its load-bearing capacity and such an important property as susceptibility to frost heaving. When choosing the depth of the foundation, it must be taken into account first.
The heaving phenomenon is caused by freezing and subsequent expansion of soil-permeating moisture.
The following types of soils are distinguished:
- rocky and semi-rocky rocks. Such a base is considered non-heaving;
- coarse and medium gravelly sand, coarse rock. They are classified as weakly heaving;
- loams, fine sand or silty sandy loam. These are already highly heaving types of soil.
To determine what type of foundation you are dealing with, soil samples should be taken by excavating a pit. Only geological engineers can provide the most accurate information, but there is also an amateur method that will help the future homeowner get the general idea.
Features of a shallow strip foundation
A shallow foundation is built most often, since the cost of materials here is the lowest and the trenches will have to be dug shallow. The minimum gap for it is about 40 cm. It can be suitable even for a two-story building if you reduce the impact of soil heaving in the following ways:
- horizontal insulation under the sole;
- vertical external insulation;
- use of pile-grillage foundation;
- arrangement of drainage;
- the use of a pillow made of non-frizz-resistant materials;
- excavation and backfilling with more durable material, such as granulated slag.
In addition, the foundation should be poured with reinforcement in order to redistribute the effect of uneven loads on the metal frame.
The economically justified maximum space limit of a strip foundation should not exceed 2.5 m. Obviously, such a design is intended for no less than a two-story building.
Soil freezing depth
In different regions, negative temperatures during the cold season penetrate into the soil to different depths. Specific data on this matter for each region can be found in SNiP “Building Climatology”.
The freezing depth values given in this document are normative.
To obtain the calculated value of this value, you should use the formula:
Df = KhDfn, where Dfn is the standard value of the freezing depth, and K is a coefficient depending on the heating mode of the building (see SNiP 2.02.01-83).
Ways to reduce the required foundation depth
There are cases when it makes sense to reduce the cost of laying the foundation to a greater depth. So, if the depth of the strip foundation for a one-story house made of foam block is not too large, then serious heavy buildings sometimes require huge costs, which developers try to reduce.
The most radical method is to completely replace heaving soil with non-heaving soil: they simply dig a pit, much larger than the design dimensions, reaching a place below the freezing line. The soil is selected, replaced with sand, and compacted thoroughly. Excavation work is large-scale, but provides a reliable result.
Blind areas can be constructed to reduce the depth of freezing of the ground and prevent it from becoming waterlogged. Blind areas are concrete platforms that run under the walls of the house and have a slope of up to 10 degrees. Their width is selected in accordance with the soil and the size of the roof overhang. So, for subsidence soils, it is enough to design a blind area up to a meter wide.
It is possible to lower the water level under the object by installing ditches with water drainage made along the slope of the terrain. The structures work well and drain water during snow melting and rainfall. If the groundwater level in the area is constantly elevated, serious drainage systems are installed.
The depth of soil freezing can be reduced by laying a special foundation made of polystyrene foam slabs under the blind area. So, if you take slabs up to 5 centimeters thick, you will be able to reduce soil freezing to a depth of 30 centimeters.
If you are building a not very massive house made of wood, you can install the foundation directly into the freezing layer. Subject to high-quality reinforcement and laying above the water line, the foundation will redistribute uneven loads and act as a single monolithic structure.
Thus, when the soil swells in one of the zones under the base, the structure does not deform, but rises, but the weight of the building holds and ensures the preservation of the plane of the foundation. Be sure to backfill the base with gravel and sand in order to smooth out uneven heaving of the soil. While a frame made of reinforced concrete will ensure the distribution of loads along the perimeter and will not allow the structure to sag.
Determining the foundation depth
Based on the data obtained, it is possible to calculate the depth of the strip foundation.
For rocky and semi-rocky soil
In this case, the foundation can be laid at any depth, regardless of how much the soil may freeze and how high the groundwater rises. Digging into such soil is often impossible due to its hardness, so the building is erected directly on top of the foundation.
For coarse rocks and gravelly sands of coarse and medium fractions
When building on sandy soil, they most often resort to constructing a shallow foundation. This is due to the ability of this type of soil to pass water well. Therefore, the forces of frost heaving are manifested in them rather weakly.
The main danger of heaving is the uneven impact on the foundation of the building, causing deformation. In the case of coarse-grained sandy soil, even with a high level of groundwater, moisture is distributed evenly, which means that even when freezing it will affect building structures equally over the entire area.
Shallow foundation
Sometimes deep foundations are very expensive to build. Then consider pile (pile-grillage) or shallow foundations (shallow foundations). They are also called “floating”. There are only two types of them - a monolithic slab and a tape.
The slab foundation is considered the most reliable and easily predictable. It is designed in such a way that it can only suffer significant damage if there are gross miscalculations in the design. However, it can also be ruined.
However, developers do not like slab foundations: they are considered expensive. They take a lot of material (mainly reinforcement) and time (tying the same reinforcement). But sometimes a slab foundation is cheaper than a deep strip foundation or even a pile foundation. So don't write him off right away. It can be optimal if you want to build a heavy building on heaving or loose soils.
Shallow foundation
A shallow tape can have a depth of 60 cm. In this case, it must rest on soil with normal bearing capacity. If the depth of the fertile layer is greater, then the depth of the strip foundation increases.
With shallow strip foundations for lightweight buildings, everything is very simple: they work well. The combination with a log house or beam is an economical and at the same time reliable option. If there are kinks in the tape, the elastic wood copes with them perfectly. A frame house feels almost as good on this basis.
You need to calculate more carefully if you are going to build the rear ones from light building blocks (aerated concrete, foam concrete, etc.) on a shallow strip foundation. They do not react in the best way to changes in geometry. Here you need advice from an experienced and, of course, competent specialist with extensive experience.
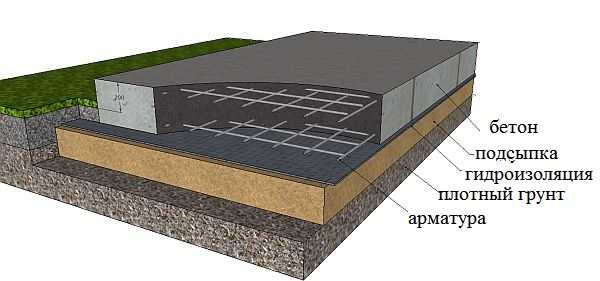
Structure of a slab foundation
But it is unprofitable to install a shallow strip foundation under a heavy house. To transfer the entire load, it must be made very wide. In this case, most likely, slab will be cheaper.
How does a shallow foundation work?
This type is used when dealing with heaving forces is too expensive and does not make sense. In the case of shallow foundations, they do not fight them. They are, one might say, ignored. They simply make the foundation and the house rise and fall along with the swelling soil. That’s why they are also called “floating”.
All that is necessary is to ensure a stable position and rigid connection of all parts of the foundation and elements of the house. And for this you need the correct calculation.
The best posts
- How to make an interior door with your own hands: manufacturing instructions (video)
- How to organize a closet inside
- How many kilowatts do you need for your home?
- Options for remodeling Khrushchev houses: 1, 2, 3, 4 rooms, before and after photos
- How to remove fungus from the walls in an apartment using folk remedies
- Mistakes when installing plastic windows
- Corrugated pipe for laying cables and wires
- Do-it-yourself partitions made of aerated concrete blocks
Related article: How to lay tiles on a wooden floor in the kitchen correctly: is it possible to lay them, instructions, video
How to minimize the effect of soil heaving
If a building is erected on heaving soil, the depth of the foundation (and the costs of its construction) can be somewhat reduced.
To do this, one of the measures should be taken to prevent the development of significant forces of frost heaving during the cold season:
- replacement of existing soil with non-heaving or slightly heaving soil: in the area of building construction, a pit is dug to the depth of soil freezing, which is covered with well-compacted coarse sand. When constructing a strip foundation, the depth in the sand, as mentioned above, can be reduced to half a meter;
- construction of drainage systems that help reduce groundwater levels;
- laying along the foundation (possibly under a blind area) thermal insulation made of polystyrene foam up to 1 m wide, which will help reduce the depth of soil freezing in this area.
Video about how deep to dig a foundation
What is the foundation depth?
The strength of the foundation is determined primarily by design features, dimensions and such an important characteristic as laying depth (DZ). It represents the interval from the base of the foundation to the zero level. The reliability and durability of the foundation depends on which civil protection structure to choose, taking into account all factors.
Having received a standard project, the developer must adapt the new foundation to specific conditions. As a result, its new design may be different from the original one.
Piles
It is especially recommended to use piles on northern heaving soils.
What is a pile foundation? When constructing this base, metal pipes with a blade at the end are screwed into the ground like self-tapping screws. Piles simultaneously support the building and distribute the load on the ground from the weight of the structure. The blade at the end of the pile prevents the structure from being squeezed out of the soil during freezing and heaving.
Such a foundation arrangement is especially relevant in the northern regions, where, due to climatic conditions and during winter freezing, the issue of squeezing out the foundations of light buildings and structures by heaving forces arises. In such conditions, piles are suitable both as a foundation for a garage and as a foundation for a one-story brick house.
For light buildings, metal bladed piles are used
How to determine the depth of foundation on piles? The depth of freezing is determined by the trenching method. The drill is screwed in to such a depth that the blades are below the freezing level in dense layers of soil.
The piles can withstand a tensile load of up to 330 Pa. In this case, the maximum pressure force during heaving is 0.2 Pa.
Metal blade piles are suitable for the construction of lightweight buildings. The technology of bored piles has been developed for heavy buildings.
The great advantage of such a foundation is that work on its construction can be carried out at any time of the year in any climatic conditions.
The strip foundation design is a monolithic, solid, inextricable concrete pour, usually with internal reinforcement.
The foundation is placed under all walls of the building, including partitions that carry vertical loads. Along the perimeter, the base has the same cross-sectional dimensions.
The foundation strip forms a continuous contour
Depending on the type of soil and the mass of the building, various shapes are poured:
- rectangular;
- trapezoidal;
- T-shaped.
The integrity and continuity of the base contour ensures uniform distribution of vertical and horizontal loads. This explains the strength, reliability and demand for this type of foundation. In addition to the shape of the base, it is important to determine at what depth to make a monolithic strip foundation. For a detailed presentation on strip foundation construction technologies, watch this video:
Shallow design is not suitable for heavy buildings
Depending on the weight of the building, the level of soil freezing, the location of groundwater and the type of soil, the depth and types of strip foundations can be different:
- shallow with a depth of no more than 0.6 m. The device is supposed to have a movable base, subject to soil heaving. Not suitable as a basis for the construction of heavy buildings;
- buried - a reinforced concrete monolithic frame laid below the freezing level of the soil. Used for buildings with basements that have a large mass.