When is protection needed?
The issue of fire safety of heating equipment is most relevant in baths and saunas .
Most often, such structures are made of solid wood. The surface of the wooden wall is close to the stove and under the influence of high temperature it begins to char over time if there is no protection. For this purpose, it is recommended to use fire-resistant sheet materials. They should mainly be in places where certain fire safety rules are not followed. This concerns the distance between heating equipment and a nearby flammable object. In cases where the distance is sufficiently large between the surface of the stove and the wooden wall, there should not be a fire. Fire safety standards provide a minimum distance:
- from a brick wall to a stove 32 cm;
- metal surface, not lined, from 1 meter;
- metal, lined from 70 cm.
In baths and saunas, where space is often limited, it is difficult to comply with safety measures. For this reason, experts recommend covering walls with non-flammable sheet materials. They will help protect walls, ceilings and floors from the source of fire and save them from fire. The materials have their own markings:
- non-flammable (NG);
- slightly flammable (G1);
- simply flammable (G2).
All materials except non-flammable ones are capable of incomplete combustion, so they burn. There are also heat-resistant and fire-resistant materials. The latter type can withstand an open source of fire quite well at close range, which is why they are often used in baths. Heat-resistant materials can withstand high temperatures well, but they cannot withstand an open source of fire.
How to protect the walls of a bathhouse from the heat of a stove - technologies and materials
When planning the construction of a bathhouse, it is important to remember to create safety indoors.
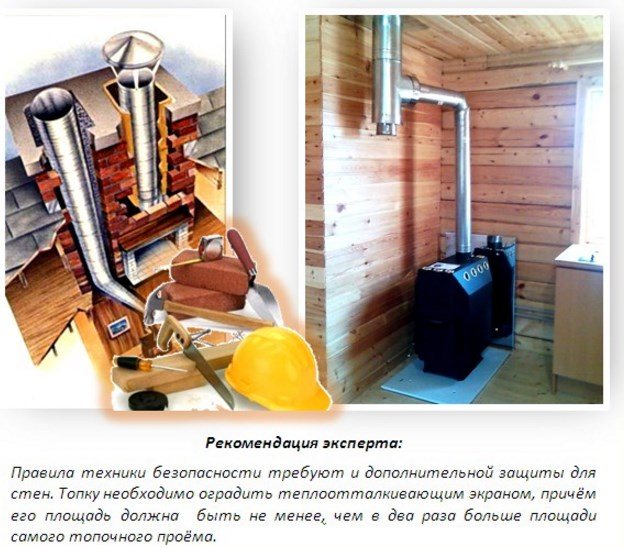
First of all, this concerns fire safety. By melting the bathhouse, the stove can be heated to 300-400°C, which significantly exceeds the combustion temperature of the wood from which the bathhouse is most often built. Protecting the walls of the bathhouse from the heat of the stove is not always required. For example, you can provide a distance between the wall and the stove, which will allow you to achieve fire safety without additional protection. The fact is that at some distance the IR rays emitted by the furnace begin to dissipate, which significantly reduces their impact on nearby surfaces.
The distance from the stove to the wall in the bathhouse varies depending on the type of stove:
- 0.32 m or more - the distance for a stone oven with quarter-brick masonry;
- 0.7 m or more is the required distance between the wall and the metal furnace lined with fireclay or brick from the inside;
- 1 m or more is a safe distance for an unlined metal furnace.
At first glance, it seems that creating such a distance is much easier than installing additional protection, but this is fundamentally wrong. Maintaining a safe distance is only advisable in large steam rooms, but in small private baths, the stove, including the indentations, will occupy most of the room, so it will be much easier to use insulation.
A feature of modern sauna stoves is their heating temperature, which can reach 400 degrees.
An important indicator of the efficiency of the furnace is instant heating of the body and maximum heat transfer.
The entire heating process is accompanied by the release of infrared radiation, which is distributed on surfaces adjacent to the furnace. Under the influence of high temperatures, the wooden structure of the bathhouse can char or ignite.
This is why it is so important to ensure that wooden surfaces are reliably insulated from the heat of the stove. A protective screen and casing made of fire-resistant materials are suitable for this.
An urgent need to install additional protective elements arises in cases of non-compliance with the fire-safe distance between the stove and the surfaces adjacent to it.
At an unsafe distance, the infrared radiation released when heating sauna stoves hits the walls and is not scattered. This leads to damage to wooden surfaces or a fire hazard in general.
So the distance from the wall to the stove:
- made of brick - 35 cm;
- made of metal (without interior decoration) – 100 cm;
- made of metal (with interior decoration made of brick or fireclay tiles) - up to 70 cm.
In small rooms where it is not possible to maintain a safe distance from the wall to the stove, it is more rational to install a protective screen or casing.
A budget option for a bathhouse is a log house, built from timber or using frame technology. Heating devices are built into partitions; the rooms have small dimensions to retain heat. Therefore, in bathhouses, comprehensive fire protection for stoves and fireplaces is used using all of the specified materials.
Fireproof cuttings with loose, sheet, and mineral wool filler are installed in the units where chimneys pass through floors and roofs. Screens are mounted on wooden walls or built around a heating device.
In the absence of specialized education, it is better to choose fire protection for stoves and fireplaces with the help of free consultations from our store employees. This will provide a number of benefits:
- construction budget adjustment
- adequate warranty from the fire protection manufacturer
- absolute fire safety of the home/bath
- selection according to specific operating conditions
- increasing living comfort
Write down the number of our specialist, add the resource page to your browser bookmarks, and call us today. This will allow you to plan your budget and avoid the risk of fire in supporting structures.
Types of fireproof materials
These materials are available in the form of slabs and panels of different sizes.
They are designed for shielding and covering various surfaces from heat sources. Fire-resistant materials are most widely used for this purpose. Fiber cement boards - they do not contain asbestos fiber, but only lightweight concrete with synthetic fiber.
Asbestos cardboard - it is produced on the basis of chrysolite asbestos, so the material can easily withstand temperatures up to +500 o C. It has a high level of mechanical resistance to alkalis and damage.
Basalt slabs and cardboard - it belongs to the category of environmentally friendly and safe materials, since it is made on the basis of basalt raw materials. It can withstand temperatures above 900 o C well and is not dangerous in operation. Most often it needs to be used with a reflective foil coating.
Minerite slabs are considered a universal material. They do not burn at all, are moisture-resistant, shock-resistant, and have excellent sound insulation. Bacteria and mold do not multiply in them.
Glass-magnesium sheets - they are made from fiberglass with the addition of magnesium binders.
Sheets of fire-resistant plasterboard - this material contains fiberglass.
Vermiculite decorative panels - they have a decorative appearance. They are made in the form of panels with different textures. They are attached using heat-resistant mastic and can withstand temperatures up to 1200 o C.
Fireproof wall coverings
If the wall of the room is directly adjacent to the surface of the stove, this leads to excessive heating of the wall, which can cause a fire. To avoid fire, the walls are sheathed with non-flammable materials.
Reflective lining
Good results are achieved by cladding that combines non-flammable thermal insulation materials and metal sheets. First, thermal insulation is attached to the wood of the wall, and sheets of metal are installed on top of it. For the outer layer, either stainless steel or galvanized is used. However, from the point of view of environmental friendliness, it is better to take stainless steel , since there is evidence that when heated, galvanized steel begins to release toxic substances.
To make the resulting cladding more effective, the steel sheet must be polished to a mirror finish. In this case, heat rays are reflected from the metal, and the wall heats up even less. In addition, the steam room receives reflected heat flows, which are softer and more acceptable to humans than those that come directly from the stove.
A number of thermal insulation materials are used for cladding:
- basalt cardboard - thin sheets of basalt fiber. This fireproof material provides not only good heat but also sound insulation;
- asbestos cardboard is a material with high thermal insulation properties. It is also fire-resistant, durable and strong;
- mineralite is a fire-resistant material from which sheets are made, used for installing protective screens for stoves and fireplaces, including in steam rooms.
The general scheme for using sheathing looks like this: wall - gap (2-3 cm) - thermal insulation (1-2 cm) - sheet of metal. This allows you to reduce the distance between the stove wall and the wall of the room to 38 cm.
The gap in the described circuit is ensured by ceramic bushings that do not heat up. If the room does not allow even the specified minimum distance between the stove and the wall to be achieved, the cladding is made with two layers of thermal insulation. A gap of 2-3 cm is left between them using ceramic bushings. Stainless steel is attached on top of the outer sheet.
Cladding with cladding
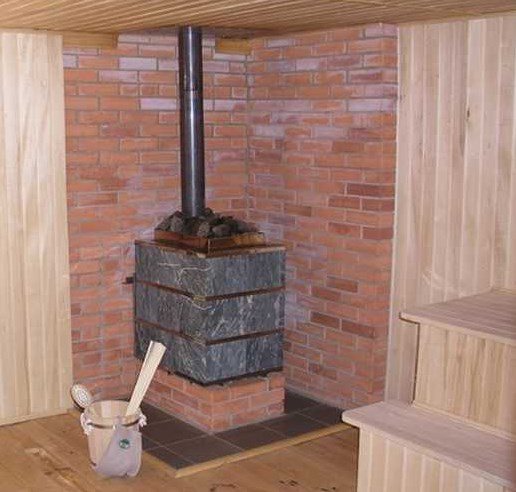
To give the steam room a more aesthetic appearance (bare iron on the wall does not look very attractive), the walls can be covered with ceramic tiles. However, if it is placed directly on wood, there will be no insulation. Therefore, the following cladding scheme is used: wall - gap (2-3 cm) - fire-resistant layer - tiles. In this case, it is allowed that there be at least 15-20 cm between the wall of the stove and the wall of the room.
Wall cladding with cladding in the bathhouse
The following materials are used for the fireproof layer:
- Fireproof drywall is drywall that has fiberglass added to it. This material is not afraid of thermal radiation and does not deform under its influence;
- mineralite is an effective fire-resistant material. Minerite fireproof boards are characterized by high moisture resistance, do not collapse or rot;
- glass-magnesium sheet is a material made from fiberglass. Magnesium substance is used as a binder. It has good sound and heat insulation, resistance to moisture and temperature changes.
The gap in the described circuit cannot be neglected, since it plays an important role. Its presence allows you to reduce the heating of a wooden wall to a minimum. The use of cladding makes the steam room look more attractive and makes it possible to maintain the design in the chosen style.
Wall cladding with sheet refractory material (PVTN)
Properly selected material for wall cladding ensures high fire safety of the room. One of the most effective for achieving this task are vermiculite panels. Vermiculite fire-resistant boards for walls are widely used to ensure fire safety of various types of premises. Their reliability is so high that this material is used in the nuclear and oil refining industries.
Advantages
The use of fire-resistant vermiculite boards allows achieving high levels of:
- environmental friendliness;
- fire resistance;
- thermal insulation;
- soundproofing;
- aesthetics.
The last point is especially worth noting. Experts know how difficult it can be to find a material that would equally satisfy the requirements of fire safety and aesthetics. Fireproof vermiculite boards are just the kind of material that is protective and at the same time has an attractive appearance. Therefore, it can be safely used in prominent places.
Application
Fire-resistant boards are used according to the multi-layer principle.
If it is necessary to perform sheathing, leave a space of 2-3 cm between the thermal insulation and the wall. The material is also glued in several layers using heat-resistant mastic. made of stainless steel sheets are most often used to insulate furnaces . This method is especially common when the stove is located too close to adjacent walls. Stainless steel sheets are often used in conjunction with non-combustible stoves. They are used as the outer surface layer. When metal sheets are polished to a shine, they tend to reflect heat. This heat flow has more gentle and gentle flows.
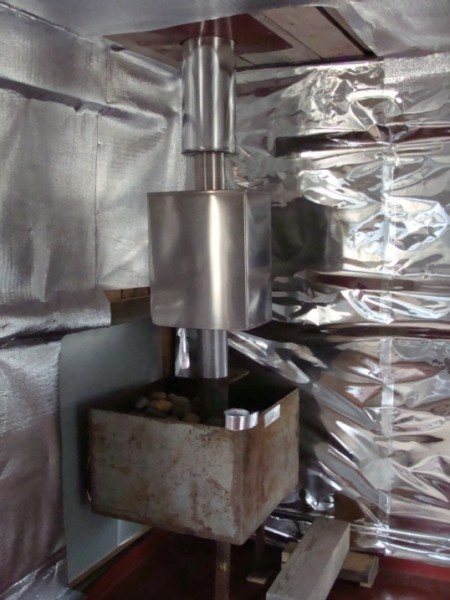
A protective screen made of steel is considered a ready-made structure. It goes around the entire surface of the metal stove on three sides. This is a very effective way to retain heat inside heating equipment. The external temperature with such a screen will reach approximately 100 o C.
Various fireproof materials, which were mentioned in the article, are used as thermal insulation under stainless cladding. Ceramic bushings are used for fastenings . Such parts allow you to form a ventilation gap between the wall and the thermal insulation, since they do not heat up.
For wooden surfaces, such cladding will serve as reliable protection against fire and heating. In this form, the cladding will not have a beautiful appearance. To make it have a more decorative appearance, heat-resistant tiles are used. It is laid using heat-resistant glue . The best facing materials include:
- clinker tiles;
- terracotta tiles;
- porcelain stoneware;
- tiles;
- Soapstone chlorite
This type of finishing is used only as an element of a multi-layer “pie” of protection. The distance between the stove and such a surface should be at least 15-20 cm . The protective layer must have a ventilation gap and fire-resistant material. The decor will make it possible to disguise the protective layer and the finishing of the bathhouse will look in the same style.
Where and how to use sheet fire protection
Sheets of material that can protect against fire are used for floors, walls and ceilings in a house where there is a source that promotes the spread of fire or in bath rooms, near a stove (heater).
Non-combustible sheet materials are used to cover the walls adjacent to the stove. A metal sheet is mounted on top of the thermal insulation attached to the wall. It is advisable to choose stainless steel, since galvanizing can release toxins when heated. For a higher heat reflective coefficient, the sheet must be in a mirror-like state. Then the heat will be better reflected from the surface and the walls will heat up less. In addition, if you use this design in a steam room, a person will receive softer and more diffused heat, which is much more comfortable than direct radiation from the stove.

For cladding with fire-resistant materials, fabrics from:
- basalt cardboard – thin sheets that have not only high thermal but also sound insulation;
- asbestos cardboard – strong, durable and heat-resistant sheets;
- vermiculite boards – noise and thermal insulation, fire resistance, environmental friendliness and effective design solutions;
- mineralite sheets are a component of the protective screen in stoves and fireplaces, including those installed in bathhouses.
The sheathing is done as follows: from the wall - a gap of 3 cm, a thermal insulation layer - 2 cm (metal sheet). This design can reduce the distance between the stove and the wall to 0.38 m. The gap is provided by ceramic bushings.
Since the metal sheet itself does not look attractive, it is often covered with tiles. What it looks like in the photo below: a wall with a 3 cm gap, fireproof padding, tiles.

Fire-resistant building materials include fire-resistant plasterboard, mineralite boards (good because they are not exposed to moisture, mold and rotting processes do not form in them), glass magnet sheets. The latter also have increased noise insulation, water resistance, heat-saving functions and do not deform under sudden temperature changes.
Fibrous refractory material: what is the surface cladding called?
According to fire safety rules, the arrangement around stoves, fireplaces and fuel boilers must be done using fire-resistant special materials, which can simultaneously protect a residential or ancillary building (bathhouse) from possible fire hitting the walls, and at the same time not cause harm to health.
To create a favorable home atmosphere, any stove or fireplace becomes very hot and generates intense heat, which in turn can be a source of ignition or fire. Therefore, it is important to carefully select the right materials when arranging a heat source in a house, bathhouse or basement, if we are talking about a fuel boiler.
Treatment of wood with fire-fighting compounds
Fire protection of a house involves treating its structures by applying special compounds to a wooden surface, or even impregnating logs or beams with them. During combustion or incandescence, the fire-resistant coating of wood begins to produce inert gases that protect the wood from fire, for example, by forming a layer of a special heat-insulating mixture.
Or preventing the access of oxygen to the site of fire. In addition to such fire-retardant impregnating compounds for structural elements protected from water, impregnation of open parts of engineering structures with a special paint and varnish composition is also used. There are also special non-flammable insulation materials for walls and ceilings that can help in case of fire.
In wooden houses, rafters, floor beams, places and structures in contact with fire hazardous elements (stove, electrical wiring, fireplace) are treated with a fire retardant compound. Then it is advisable to process all frame partitions and all interfloor ceilings. Voids in structures are stimulants for the spread of fire during a fire; they cause draft and “stretch” the fire, heating up the fire.
Types of materials
Refractory materials can be roughly divided according to the method of heat transfer:
- Heat reflective – aimed at reflecting infrared radiation into the room;
- Preventing loss due to its physical and chemical properties.
On video of fireproof materials for walls around furnaces:
But all of them can also differ in the type of raw materials from which they are produced:
- With organic components , for example, polystyrene foam materials, although their fire resistance is very low, they are best suited for walls near stoves with low heat;
- Inorganic is a broad class of non-combustible materials for insulating walls of a wide variety of fire resistance, including very flammable ones, such as wooden floors. These include stone and basalt wool, pressed into large slabs, fiberglass wool, lightweight cellular concrete slabs with fire retardant impregnations, honeycomb plastics, foamed perlite or vermiculite, and polypropylene. However, such a beautiful decorative thing as Leroy Merlin sheet plastic is definitely not suitable.
- Mixed type - these include asbestos-cement refractories, asbestos-lime or silica, foamed from a variety of inorganic substances.
Basic requirements for refractory materials
Many country buildings are built from wood, be it a cylindrical or frame house; without a stove or fireplace it is difficult to survive a frosty winter, so their arrangement is approached very carefully, and the materials placed around the stoves are chosen so that they are:
- Effectively and reliably prevented any attempted fires;
- Environmentally friendly, so that when heated they do not release harmful substances into the home air.
Information from this article will help you understand what composition of mortar for plastering a stove exists and is most often used.
But what are the dimensions of a standard oven brick can be seen here.
Non-flammable materials for baths: we ensure maximum safety during operation
When planning the purchase of bricks, insulation or boards for cladding, it is necessary to allocate fire-fighting materials in a separate column of our list: for a bathhouse, fire protection is one of the priorities, and therefore you should not skimp on it.
Below we will talk about fire safety standards for the design and construction of baths and saunas, and also describe the most commonly used fire-resistant products.

It is very important to protect the building and its finishing from high temperatures
Wooden houses: insure, be sure to insure...
• electrical wiring is made of double-insulated wire; • fireplaces, stoves with cracks, faulty doors and drafts are not used; • floors, walls and partitions have the necessary fire insulation; • there are electrical supply projects approved (by the relevant authorities with approvals and permits) , heating, all necessary permits.
Traditionally, insurers insure a wooden house against risks: explosion, lightning, fire, flood, natural disaster, theft (burglary), robbery, robbery, falling trees (poles), collision with a vehicle. A full package of such insurance for a wooden house will cost approximately half a percent of the market value of the house. Please take into account that the possible damage from a fire will not be much less.
Causes of fires
During operation, the bath structure itself and its individual elements are systematically exposed to high temperatures. And in some cases, this exposure leads to fire.
The main reasons for the appearance of an open fire are:
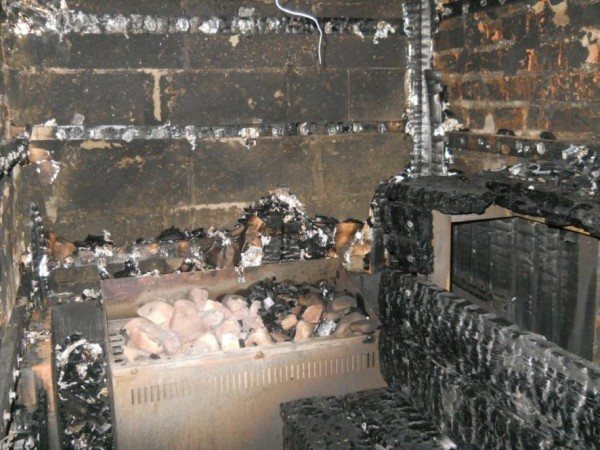

Photos of the consequences of fire safety violations
Note! If you are using an electric heater, you should protect it from short circuits by connecting it to the distribution panel through a residual current circuit breaker.
- However, the main reason why a fire can start in a bathhouse is the use of unsuitable materials in the finishing. Contact of untreated wood or plastic with a heated surface will, at best, cause smoke, and at worst, lead to burnout of the entire structure.
Fire automatics
Installing a fire safety system is your choice; it is not a mandatory element for everyone. This is a desirable system. But if you decide to install such a fire protection system, then this should be done in accordance with all the requirements of the relevant standards and SNiP. Only this will ensure their maximum effectiveness. Half solutions are ineffective.
Numerous practical cases indicate that a timely signal about the start of a fire will prevent a more destructive fire. The damage from such a fire is not comparable to the resources, both monetary and mental, sufficient to install a fire safety system. If you “save money” on this, then the most disastrous results are possible.
It must be taken into account that, for example, by installing the simplest and most inexpensive smoke detector in distribution cabinets of electrical networks, you can prevent the fire itself and reduce the likelihood of a fire. In any home, according to statistics, the main source of household fires is electrical wiring. It should be well arranged, well insulated.

In a country house, you can also install a fire sensor in technical fire-hazardous rooms. This is a boiler room, a garage, a flight of stairs, a cold storage room and other rooms. If an electronic fire alarm system is installed, then for its effectiveness it is necessary to have reliable (serviceable, in working order) primary fire extinguishing equipment (fire extinguishers, a shovel, a hook, a box of sand). This is provided for by the basics of fire safety and will not require any great effort.
it has a low price (compared to other types of fire extinguishers), it is easy to maintain, and it is environmentally friendly. Most of these modules can operate in electric auto-start mode (based on a fire sensor signal) or in self-start mode (if the temperature rises to a critical value, the value of which was initially set in the system). Such modules have a place in fire-hazardous technical rooms (boiler room, garage, etc.).
The powder module, complete with electronic control, stands out as a separate automatic fire extinguishing system. It can also act as an integral part of a fire security system if its output is combined with the input of an automatic fire extinguishing system. Recently, the concept of “smart home” has been used.
Materials
Structural features
It is necessary to choose fireproof materials for a bath taking into account exactly where they will be used. Below we will try to analyze the main groups of materials depending on their purpose, and we will try to highlight those that have advantages in terms of fire safety.
The building itself can be erected:
- Made of wood - timber or logs. Despite the numerous advantages of natural raw materials, wooden baths are quite dangerous in terms of ignition and flame spread. If the temperature inside reaches a critical level, then even wood impregnated with fire retardants will sooner or later catch fire.
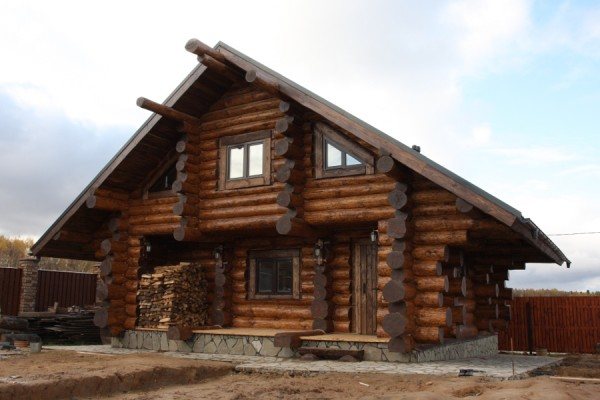

Wooden buildings must be treated with fire retardants
- Even more dangerous are frame models. The thing is that even when using fire-retardant fillers, there is air inside the frame, which contributes to the fairly rapid spread of flame.
Note! If we take into account that frame structures retain heat very moderately, then their only advantages will be their affordable price and ease of installation. However, when it comes to a bathhouse, such savings cannot be called justified.
- Building blocks (cinder block, foam concrete, aerated concrete, etc.) are much safer. They not only do not burn themselves, but also significantly limit the spread of flame due to their high thermal insulation ability.
- An excellent option in terms of fire protection is masonry walls made of red brick. Even ordinary varieties of this material resist heat well, so you don’t have to worry about the structure itself.

Building blocks are not so beautiful, but they are safe
In addition to the walls, attention must also be paid to the roof and other structural elements. In most cases, you cannot do without wood, so impregnation with a fire retardant compound will still be needed. And roofing materials should be selected with minimal flammability ratings - metal tiles, Euro slate and similar varieties are suitable.
Brick for the stove
The stove is the heart of any bathhouse, and therefore its masonry should be given the closest attention. If you do not use ready-made steel or cast iron models, then a brick structure will heat the air and water in the steam room.
When laying a stove, experts strongly recommend using the most heat-resistant material for a bathhouse - refractory brick.
Today, the following types of blocks for laying stoves are popular:

- Alumina brick (so-called fireclay) is the most popular and in demand type. Its main advantage is that during sudden cooling (for example, when water gets on hot masonry), the blocks do not crack.
- Quartz stone resists heat well, but with prolonged contact with metal (sauna firebox, water tank, doors) it can lose its properties and begin to delaminate.
- The main one is made from alkaline lime raw materials with the addition of magnesium sulfate. It is used in metallurgy, it is quite expensive, but it “holds” the temperature perfectly.
- Carbon - pressed from coke or graphite raw materials, able to resist even the strongest heat. However, the high cost and rather unusual black color significantly limit its use in laying stoves.
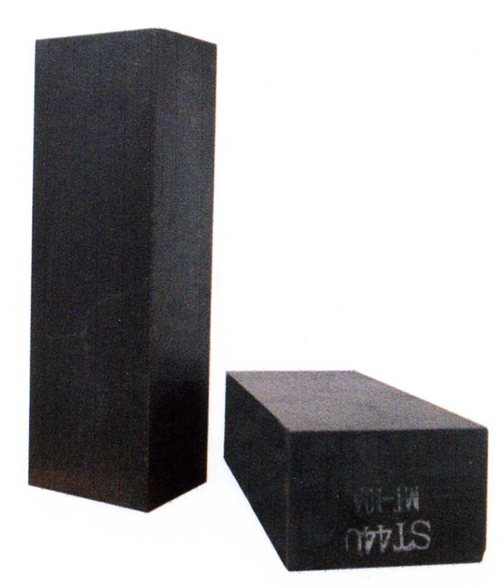

Carbon building stone
If you do the laying yourself, it is very important to prepare the solution correctly.
It must not only reliably hold the building blocks together, but also withstand high temperatures well:
- The classic option is a solution based on fireclay (light) clay with a small addition of sifted fine sand. After heating, the clay is baked and over time acquires a strength slightly inferior to the strength of the stone itself.
- More modern instructions recommend using special heat-resistant adhesive mixtures. These compositions are characterized by low shrinkage rates, which is why the seams between the rows are quite thin. And this, in turn, has a positive effect not only on fire safety, but also on the efficiency of the furnace as a whole.

Safe finishing
However, it is most important that fire-retardant materials for the bath are used in the interior decoration. And this is quite natural - almost 100% of fires start due to a fire in the steam room in the immediate vicinity of the stove.

- Firstly, to protect against fire, the bathhouse lining from which the internal lining is made must be impregnated with special compounds. Ideally, this is done in production by pumping fire retardants into the chamber under high pressure.
- However, if you were unable to purchase a pre-treated board, you can always apply the protective mixture yourself. For application, you can use either a brush or a spray gun - the main thing is that all parts are covered evenly.
- Secondly, in addition to decorative cladding, it is important to choose the most suitable insulation. Polystyrene and foam plastic boards used in the decoration of residential buildings are not suitable: if they do not burn, they melt with the formation of a large amount of toxic smoke.

Insulation based on basalt fiber
- One of the suitable thermal insulators is mineral wool. Modern modifications based on mineral fibers are characterized by sufficiently high heat resistance, which allows them to be installed in the hottest saunas.
Note! A good alternative to regular mineral wool is basalt wool. Mats based on basalt fiber can withstand heating up to 750 0 C, so they are definitely not afraid of an accidental spark.
- Ecowool - cellulose fiber with special impregnation - is somewhat inferior to mineral heat insulators, but can also be used. Of course, for the steam room itself it is better to choose a more reliable insulation, but you can fill the space under the lining of the dressing room or rest room with ecowool without fear.

Although ecowool ignites, it goes out quickly
- Foil materials are an essential component of an effective fire retardant finish. The aluminum foil used in them reflects a significant part of the heat rays into the room, which means that the material under the metal layer will heat up minimally.

Foil lining is very effective
Advice! In bathhouses, it is better to install foil film with a thin polymer base - this way there is less risk of it melting when overheated.
Cladding with cladding
This option is practically no different from the previous one, however, if you don’t know how to decorate the wall behind the stove in the steam room in such a way as to preserve the beauty of the room while creating safe conditions, then this option is undoubtedly for you. Protect the walls using heat-resistant decorative materials laid on thermal insulation.
The finishing around the stove in the bathhouse can be done with the following materials:
- Clinker tiles are made from baked clay. It is characterized by high strength, heat resistance and durability. One of the advantages of this option is also the rich color palette, which includes not only black and white tones, but also blue or green colors;
- Terracotta tiles are also made from clay, but they are inferior to the previous option in terms of density and the number of possible colors;
- Soapstone is a good cladding option for a bathhouse, made from rocks of green and grayish shades. Has good heat resistance and strength;
- Tiles are ordinary ceramic tiles, characterized by good heat resistance and a pattern on their surface;
- Porcelain tiles are heat-resistant tiles that imitate natural stone or wood.
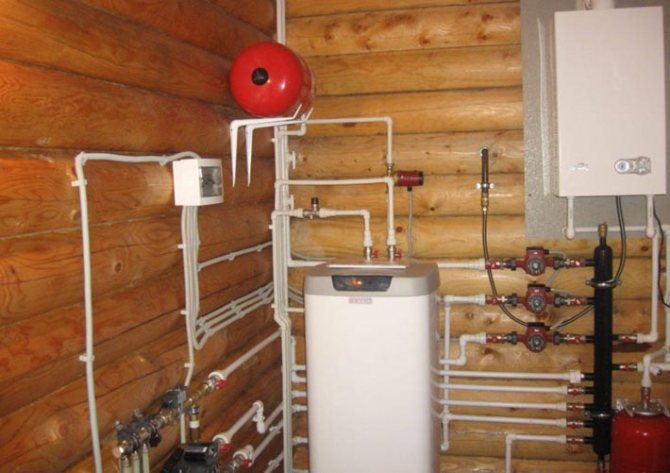

The tile will not dissipate heat, protecting the walls from fire, so it cannot be mounted directly on the wall. We recommend using the following design:
- Wall;
- Clearance for ventilation;
- Fireproof material;
- Tiles (the distance from the tile to the stove must be at least 15 cm).
Such a “pie” will create reliable protection for walls from heat, preserving the beauty of the room.
One of the following options can be used as a fireproof material:
- Fireproof drywall - made from the same materials as regular drywall, but using fiberglass;
- Minerite slabs for baths are absolutely not exposed to moisture and heat.
- Glass-magnesium sheet - plates made of fiberglass and magnesium binder. Excellent resistance to heat, moisture and noise.
This option will perfectly protect your bathhouse from the possibility of fire, and will also insulate the room, preserving its aesthetic component.
Non-combustible finishing and thermal insulation of the bath
It is known that during the operation of modern baths, the walls of steam rooms adjacent to the stoves heat up to approximately 400 degrees. As a rule, they are finished with wood materials, which under certain conditions can begin to char.
To avoid trouble, special techniques have been developed to protect these parts from thermal destruction. In baths and saunas, various fire-resistant and non-flammable materials are used for finishing and insulation, which, in addition to their protective properties, should also have a certain attractiveness.
Insulation of steam rooms
In addition to protecting the surfaces adjacent to the stoves, baths (steam rooms) and saunas must be provided with reliable insulation to ensure that the required temperature is maintained.
To insulate steam rooms from the inside, the following techniques can be used:
- the use of heat-insulating non-combustible materials that are most suitable for areas of high humidity in the bathhouse (usually stone or mineral wool is used for these purposes);
- arrangement of vapor barrier protection;
- creation of screens based on non-flammable aluminum foil.

Before starting insulation work, you should prepare the surfaces for laying the selected type of heat-insulating material, which is spread in the niches of the sheathing. A vapor barrier layer is installed on top of the insulation, which can be used as an ordinary polyethylene film.
A special foil film, spread directly on the insulating layer, is also suitable for arranging such protection. Currently, special types of thermal insulation material with a foil layer already present on their surface are on sale.
Decorative lining is placed on top of protective coatings and films, which can be ordinary lining, most common in a bathhouse, or any other heat-resistant material.
Protective materials and devices
When choosing protective screens based on sheet blanks for a bath or sauna, the following range of special products offered on the domestic market is taken into account:
- non-combustible asbestos boards;
- steel sheets;
- calcium silicate and other special protective screens, panels, slabs.
According to the requirements of current standards, the need for such non-combustible materials arises only in cases where the distance from the stove to the walls of the bathhouse does not meet fire safety standards. For different types of ovens they vary from 32 cm to one meter.
Sometimes stoves in modern baths are finished with non-flammable tiles made of ceramic or stone. As for wooden materials for decoration and accessories, they all have low thermal conductivity, therefore, although they are not non-flammable, they heat up weakly. For the construction of baths, wood with anti-perenum impregnation, brick, aerated concrete and other non-combustible material are used.
Asbestos sheet
Asbestos belongs to the category of fire-resistant, non-combustible materials that can withstand prolonged heating without loss of strength up to temperatures of about 450-500 degrees.
It can have a variety of designs, including sheet format (in the form of blanks of standardized size). This material is in particular demand in places that are subject to reliable insulation from high-temperature influences (in rooms with thermal and heating stoves installed in them, in particular in baths).
In addition, special fire-resistant partitions for walls and ceilings in bathhouses, as well as insulation of pipelines and thermal connections, are made from asbestos sheets.
Sheet steel and protective screens
Sheet steel is often used as a protective coating for walls in steam rooms, the condition of which is subject to special requirements.
For these purposes, only high-quality metal that is not damaged by rust, purchased in the form of sheet blanks, should be used.
Often, steel sheets are used in bathhouses and to protect floor coverings directly adjacent to the stove, and are used as material for stands.
Protective non-combustible screens are structures that provide insulation from the side walls of the combustion unit in the bathhouse.
They are made of brick or metal sheets and mounted at a distance of no more than 5 centimeters from the surface of the stove walls. From a practical point of view, non-combustible screen structures made from steel blanks or fire-resistant glass are of greatest interest.
Fire-resistant slabs made on the basis of calcium silicate are considered more modern materials for finishing baths. They are used to insulate the walls of the stove in the bathhouse and exhaust ducts.
Protective screens for furnaces
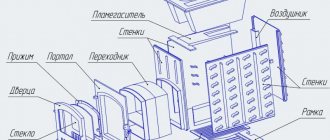
Protective screens are structures used to insulate the side walls of furnaces. They reduce thermal radiation. Protective screens are made of brick and steel. Mostly such designs are used for metal furnaces.
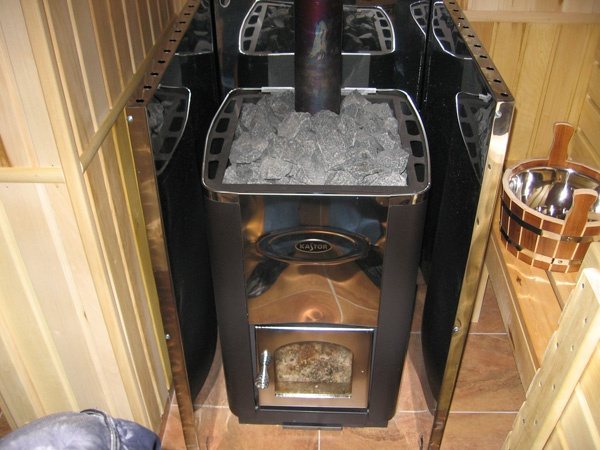

Oven with metal protective screen
The easiest way to build a protective screen for a furnace with your own hands is from sheets of cast iron and industrial steel. Such screens are the most common. The sheets are installed at a distance of 1-5 cm from the walls of the oven.
Screens can be either side or front. There are furnace designs that do not require protective screens. They already have a special casing that reduces the intensity of thermal radiation.
Internal impregnations
The main reason for using special impregnations in baths and saunas is increased levels of humidity and temperature, which can cause destruction of wooden ceilings, walls and shelves.
When choosing an impregnating material suitable for these purposes, the main attention is paid to the quality of the composition, after application of which the wood should not lose the ability to “breathe” freely.
You should also distinguish between the types of compounds used to protect shelves and benches from similar materials used when treating walls and ceilings in a bathhouse.
Impregnation for shelves
The protective agents used to treat shelves, based on their effect on the color of the wood, are divided into colorless and colored.
The first includes impregnations of various compositions, bleaching mixtures, varnishes and waxes. Varnishes for the protective coating of shelves in saunas and baths must be subject to strict selection, during which special brands that release toxic substances when heated are eliminated. Typically, for benches and shelves in a bathhouse, water-based compounds are used that penetrate well into the wood structure.
Colored coatings are used in cases where darkening of previously treated areas is observed. In this case, only the tarnished parts of the surfaces are subject to coating, but if desired, they can be completely treated.
As for specific samples of protective material, acrylic varnishes from these or “Belinka” are suitable for treating baths and saunas. All of them are made on a natural basis and have a large selection of color shades.
Protective coatings for walls and ceilings
Impregnations intended to protect walls and flows in the bathhouse must have an organic base and have water-repellent properties.
Modern processing agents have universal properties and are able to protect surfaces from moisture and thermal heating, as well as from the destructive effects of fungi and insects.
Depending on their base, all known types of protective impregnations are divided into water-based and oil-based preparations. Complex (combined) compositions, produced in the form of paints and varnishes, are also very popular, providing protection for the finishing materials of the bathhouse from moisture fumes and microorganisms.

Some of them have additional features such as fire resistance and the ability to repel dirt.
Heat resistant cables
Choosing a non-flammable cable for steam rooms is a fairly responsible procedure that affects not only the operational reliability of the installed wiring, but also the safety of people in the bathhouse.
Since the temperature inside the steam room can reach plus 170 degrees (with a humidity level of up to 90 percent), the cable products installed in it must have the appropriate characteristics. For these purposes, it is recommended to select special samples of waterproof and heat-resistant cable products in a non-flammable sheath, the quality of which is confirmed by certificates.
Thermal insulation for pipes
In the absence of insulation of pipe outlets, due to a large temperature difference in places where combustion products are discharged, condensation may form, which can destroy adjacent parts of the wooden structure.
In addition, well-insulated exhaust channels will work much more efficiently, preventing heat from escaping from the room.
Depending on the design of the chimney, a variety of materials can be used for its thermal insulation. The most common type of non-flammable insulator suitable for pipe insulation is double-wall pipes (sandwich) made from stainless steel.
To preserve heat in the bath and insulate pipe bends, special non-flammable ceramic sections mounted in expanded clay concrete modules can also be used.
Mandatory protection of the interior spaces of bathhouses from exposure to high temperatures and humidity has two goals. Firstly, this ensures the safety of the wood surfaces inside and, secondly, it increases the operational safety of the entire structure as a whole.