Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated December 20, 2013 N 70 “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.2. 3150-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the placement, design, equipment, maintenance and operating hours of baths and saunas”
In accordance with the Federal Law of March 30, 1999 N 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 1999, N 14, Art. 1650; 2002, N 1 (Part 1), Art. 2; 2003, N 2, article 167; N 27 (part 1), article 2700; 2004, N 35, article 3607; 2005, N 19, article 1752; 2006, N 1, article 10; N 52 (Part 1), Article 5498; 2007 N 1 (Part 1), Article 21; N 1 (Part 1), Article 29; N 27, Article 3213; N 46, Article 5554; N 49, Article 6070; 2008, N 24, Article 2801; N 29 (Part 1), Article 3418; N 30 (Part 2), Article 3616; N 44, Article 4984; N 52 (Part 1), Article 6223; 2009, N 1, Article 17; 2010, N 40, Article 4969; 2011, N 1, Article 6; N 30 (Part 1), Article 4563; N 30 (Part 1), Article 4590; N 30 (part 1), Article 4591; N 30 (Part 1), Article 4596; N 50, Article 7359; 2012, N 24, Article 3069; N 26 , Art. 3446; 2013, N 27, Art. 3477; N 30 (part 1), Art. 4079; N 48, Art. 6165) and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2000 N 554 “On approval of the Regulations on state Sanitary and Epidemiological Service of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on State Sanitary and Epidemiological Standardization" (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2000, No. 31, Art. 3295; 2004, N 8, art. 663; N 47, art. 4666; 2005, N 39, art. 3953) I decree:
Approve sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.1.2. 3150-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for placement, equipment, maintenance and operating hours of baths and saunas” (appendix).
Acting Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation
Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 13, 2014.
Registration N 32244
Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the placement, design, equipment, maintenance and operating hours of baths and saunas have been developed (SanPiN 2.1.2. 3150-13).
Objects must be located in separate buildings. They cannot be installed in multi-apartment residential buildings. The internal layout should be such as to ensure the sequential progression of visitors according to the following scheme: wardrobe, dressing room (they are equipped with bathrooms), soap room, steam room. It is possible to organize manicure, massage, catering, retail, etc. services. It is possible to install a swimming pool.
It is necessary to equip facilities with hot and cold water supply, sewerage, heating, and ventilation systems. Air conditioning is allowed. Cleaning and disinfection of mechanically driven supply and exhaust ventilation systems should be carried out at least once a year.
To decorate premises, you need materials that are resistant to moisture, temperature, detergents and disinfectants. Furniture should have smooth surfaces.
Microclimate parameters have been established: in the dressing room - air temperature is 25-28°C, in the soap room - not lower than 25°C.
There are special requirements for individual rooms, including linen rooms and staff rooms.
Routine cleaning should be carried out throughout the working day. Deratization and disinsection - at least once a month.
Employees must undergo preliminary (upon employment) and periodic medical examinations, and certification of knowledge of sanitary rules at least once every 2 years. A medical card is issued for everyone.
Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated December 20, 2013 N 70 “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.2. 3150-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the placement, design, equipment, maintenance and operating hours of baths and saunas”
Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 13, 2014.
Registration N 32244
This resolution comes into force 10 days after its official publication
The text of the resolution was published in Rossiyskaya Gazeta dated May 22, 2014 N 113
Bathhouse services are quite in demand due to national traditions and are regulated in detail by current legislation and regulations.
The requirements imposed by Rospotrebnadzor for public baths are of a general nature, regardless of what class of service provision it belongs to - a bathhouse or a shower.
Classification of baths
In Russia they are classified according to a number of criteria:
- First of all, technological:
- The services provided by the baths are divided according to the type of steam room available (they are usually divided into national ones: Finnish, Russian...), as well as by the presence of a swimming pool or its absence;
- Services provided by showers. Can be provided in closed cabins with a bathtub and shower installed there;
- Services of complexes that are bathing and recreational;
- Secondly, by the type of available services provided:
- Baths used as: hygienic, combined, mobile, access;
- Separate showers, equipped in the building occupied by the bathhouse, or located in a separate building;
- Complexes used as bath and health facilities;
- According to the association of users, baths are divided into:
- Public baths;
- personal (individual use);
- bathhouses for group use;
- Fourthly, according to the form of available service, baths are divided into:
- permanently located;
- designed to provide on-site service;
- Fifthly, in terms of quality of service. Existing baths are divided into establishments by category:
- Highest category;
- 1st;
- 2nd;
- Departments with cabins for providing bath and shower services, 1st category;
- 2nd category;
- Rooms divided into rooms of the highest and first category.
Main regulatory regulations
The requirements of the SES are organically linked to the provisions of current legislative and by-laws, departmental documents and standards. Among the main documents it is necessary to note:
- registered under No. 2.1.2.3150-13. The text was approved by Decree No. 70, issued by the Acting Executive Office of the State Service for Military Inspection of the Russian Federation on December 20, 2013. regulates a set of requirements for baths of various types;
- rules number 2.1.2.1188-03. They set out the requirements for the quality of water that fills the pool (if any);
- 2.1.4.1074-01. The document, as amended on June 28, 2010, regulates the requirements for cold water supplied to the bathhouse;
Standards for the construction of a bathhouse
Advice from lawyers:
1. Tell me where to write an application with a request to check fire safety standards during construction on a garden plot... this is the Gatchina district. A neighbor is building a house... large and wooden. The distance from my bath house is 7 meters. According to SNiPs, the distances between wooden houses are 15 m. security is also 15 meters. I want to understand whether the burrows are disturbed?
1.1. Contact the Gatchina District Prosecutor's Office with a corresponding complaint about conducting an inspection.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
2. When contacting the architectural department for the construction of an auxiliary facility, they said that a building permit was not required. We built a garage and a bathhouse and violated city planning regulations. We were denied permission to build a house. What should we do.
2.1. Good afternoon. Receive a refusal and appeal it in court. In general, it is necessary to read the application with which you applied and, naturally, the refusal to it. Sometimes it happens that an incorrectly written application results in a 100% refusal. You need to contact a lawyer with documents for a face-to-face consultation.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
3. Two years ago we purchased a residential building with a bathhouse on the site. The bathhouse burned down the other day. An investigator came and concluded that norms had been violated during the construction of the bathhouse. Namely, the pipe was not insulated from the furnace. The question is: can we recover financial damages from the seller?
3.1. Good afternoon You can file a Statement of Claim with the Court. Article 3 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. Right to go to court 1. An interested person has the right, in the manner established by the legislation on civil proceedings, to go to court for the protection of violated or disputed rights, freedoms or legitimate interests, including with a request to award him compensation for violation of the right to a trial within a reasonable time term or the right to execute a court order within a reasonable time. 2. Waiver of the right to go to court is invalid.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
4. We are building a bathhouse on our site, we started digging a hole. The neighbors’ window (private house, distance about 100 m) overlooks exactly this place. They came and began to say that the smoke from the bathhouse would go out of their window and that we had no right to put our bathhouse there. They promised to sue. How should we deal with this situation and what are the standards when building a bathhouse?
4.1. Anna, if this is a private house, it is located about 100 m from your bathhouse under construction - this distance is more than enough. The neighbors will be denied permission to go to court.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
5. A neighbor in the garden built a bathhouse and a house almost adjacent to the common fence, which led to strong shading of the entire plot; if we sell, our plot will depreciate by a considerable amount. Access to sunlight to the site is greatly reduced. What is the right thing to do in this situation? During construction, he was repeatedly asked to comply with regulations, i.e. retreat 3 meters from the common fence.
5.1. Dear Valentina, Ufa! According to Article 304 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation Protection of the rights of the owner from violations not related to deprivation of possession. The owner may demand the elimination of any violations of his rights, even if these violations were not associated with deprivation of possession. Therefore, I recommend that you go to court regarding this violation. Good luck to you Vladimir Nikolaevich Ufa 06/13/2017
Did the answer help you?YesNo
6. We want to buy a house in the village. The seller has documents for the plot and the house. House in the village, land category private household plot. But at the moment there is a garage attached to the house and a bathhouse built on the site; there are no documents for them. What does this mean for us? Will we be able to register them in our name? What fire safety and technical standards had to be observed during construction? Thank you.
6.1. Dear Olga! In theory, it is not necessary to register these buildings; in practice, few people do this. Of course, you can register, according to building codes, outbuildings must be at least a meter from the property line, and the house itself must be at least 3 meters away.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7. Our neighbor built a bathhouse along the boundary (we gave consent), but during construction he climbed onto our site and the roof drain was on our territory, about 30 cm plus the wall of the bathhouse itself. He doesn’t want sewerage and doesn’t want to communicate at all, can we demand through the court that he move his bathhouse, not only partially but also completely according to the norms, will our consent matter?
7.1. Yes. Of course you can. You will have to go to court with a claim to remove obstacles to the use of your land plot.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7.2. Your issue can only be resolved in court.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7.3. Your consent will be important in terms of moving the bathhouse to the border of the land plot, and the neighbor will be required to arrange the drain in such a way as to prevent water from entering your plot. If you need help, you can contact us.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
8. I wanted to know if permission from neighbors is needed when building a bathhouse, which will be 1 m from the boundary according to the standards?
8.1. No. no permission needed.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
9. What are the fire safety standards for the construction of a public bathhouse in the private sector?
9.1. Hello! See SNIP “Rules for the development of urban and rural settlements”.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
10. What fire safety standards exist when building a bathhouse on your own territory and with neighbors? This means in meters.
10.1. Read the Code of Rules SP 42.13330.2011 “SNiP 2.07.01-89*. Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements" at the link Read more >>>
Did the answer help you?YesNo
11. The neighbors built a house and a 2-story bathhouse and rent them out. They often heat and make noise in the evenings. We have a lowland and we can’t breathe from their bathhouse. The purpose of the land is either individual housing construction or private plots. Construction standards were not met (the house is close to the fence on both sides of the neighbors (the plot is narrow), there is a barbecue between the bathhouse and the house, everything is in close proximity). Requests to stop are not responded to. What should we do, where should we go, what are the standards for commercial baths in the private sector? Thank you in advance!
11.1. Hello. File a complaint with the local administration and the tax office (if they are not formalized).
Did the answer help you?YesNo
12. Without retreating from the neighboring plot, on the border with them I built a garage, a house, a bathhouse, all under one roof, the length of the building was 20 m. The neighbors were silent. Now, after the flood of 2014, I began to build a summer version of the 2nd floor along the entire length of the building. The neighbors' house on their property is still 3 meters away, but they were outraged and promised to sue. Allegedly, water and snow from the roof are in their fence. Are they right? And are there any standards for the construction of neighboring houses? They were built (neighbors) in 1961, and ours was built in 2009.
12.1. It is necessary to study the title documents; disputes related to the use of land require careful analysis.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
12.2. Send a notice to neighbors, offer drainage options, and indicate all conditions. The court will examine the extent to which your construction violates the rights of your neighbors. You can also go to court, removing the obstacles that your neighbors create for you, you have the right to dispose of your land, house, etc. you have the right to build, but without violating the rights of third parties.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
13. How should I behave when examining a wooden bathhouse made of timber between my organization and the customer? I hired an expert to explain that the building standards were violated and this prevents the commissioning. Construction was carried out according to the plan. People, having experience, built an object as an individual. As a guarantor, I entered into an agreement with the customer on behalf of the organization. The beneficiary is an individual. How to properly conclude a relationship with an individual and represent my interests to the customer? Thank you.
13.1. If you hired an expert, then you don’t have to behave in any way with him. He himself must know what he needs to do and how.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
14. The expert answered negatively to the question about violations of urban planning standards and fire breaks, during a forensic examination of the unauthorized construction of a house. The defendant built a house with an attached garage and boiler room at a distance of 0.5 meters from the border of my plot on the side of the garage and boiler room and at a distance of 3.6 meters from the neighbor’s bathhouse. Can I sue an expert for knowingly false examination?
14.1. Not a lawsuit, but a statement to the police.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
14.2. It is impossible to prove that the conclusion was deliberately false. If you have a legal dispute, then you need to apply for a second examination, or perhaps do the examination yourself.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
15. A neighbor built a bathhouse on the coastline where all construction is prohibited, violating the law on dacha construction and the SNT charter, without having any of the permits, while violating all fire safety standards, about which an act of the Ministry of Emergency Situations was drawn up, what should I do next to liquidate this bathhouse? .
15.1. Excuse me, but who are you? The owner of a land plot whose rights have been violated by an unauthorized construction (bathhouse) has the right to appeal to the court.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
15.2. All you have to do is write complaints to the prosecutor's office, etc.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
16. The question is related to the standards for indentations during the construction of a bathhouse. There are several options for laying the foundation, but: an overhead gas pipe runs along one of the boundaries with the neighboring site; a garage has already been built on the neighboring plot, a meter from the border; 3rd option - the neighbor’s house is nearby. What standards are there and which SNiP to follow?
16.1. It depends on the purpose of the site (individual housing construction, country house, garden, private household plot, etc.). There are different building rules for different areas, for gas pipes, it also all depends on its type.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
17. What standards must be observed on earth. plot in gardening during the construction of a house, garden house, outbuildings?... and what is the best thing to do so that, in addition to a solid residential house with a foundation, not to register a garden. house, barn, bathhouse... And if you build a garden. house now and planning to convert it into a bathhouse in a couple of years, should it be registered as a house now? Thank you.
17.1. When designing the development of territories of horticultural and dacha non-profit associations of citizens, one should be guided by the Code of Rules SP 53.13330.2011
Did the answer help you?YesNo
18. The land plot is owned, but not large in size - 7 acres. How to comply with all construction standards if we plan to build a house and a garage, a utility block and a bathhouse, but then all the buildings will be located close to neighboring plots. Will there be any problems obtaining a building permit? If yes, how to avoid them. Thank you.
18.1. Good afternoon. If the buildings are less than 4 floors, i.e. three (together with the basement), then you do not need any building permits. The land is yours, build where you want, taking into account the purpose of your land plot.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
19. The neighbors built a bathhouse near his garden, infringing on our interests. Construction was carried out with the connivance of the head of the local administration. After we filed a complaint with the court, they decided to conduct an examination to verify compliance with architectural, fire safety, and environmental standards. The head of the local administration was authorized to draw up a diagram of the location of buildings on personal plots, with whose connivance the construction of the bathhouse was carried out. Is this legal? Thank you.
19.1. What's the difference? After all, the question is whether the diagram is drawn up correctly or incorrectly, that is, whether the physical parameters indicated on the diagram (distances, height, length, etc.) will correspond to the actual ones. It is difficult to convert such parameters. Well, if they don’t comply, you can declare this and demand the drawing up of a new scheme that corresponds to the actual situation.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Requirements for bathhouse premises
Based on clause 5.9 of standard 32670-2014 (see above), it is recommended to have the following rooms (compartments) in the bathhouse:
- Bathroom section:
- Steam room;
- Common washing area with open showers;
- Possibly a mini-pool (optional);
If we are talking about bath and health complexes, they may have:
- Prevention department, which also offers wellness services;
- Bathroom section, equipped with showers and steam rooms for group or single use;
- Children's department;
- Possibly a swimming pool;
- Other options.
Sanitary rules 2.1.2.3150-13 set out the requirements that bathhouse premises must meet:
Interior finishing work can only be carried out using materials that have significant resistance to:
- exposure to cleaning agents and disinfectants;
- high temperatures (in steam rooms up to 110°C);
- significant humidity;
In the changing rooms, each person washing is provided with his own hanger and a separate place. It must be possible to deposit valuable items belonging to the client. The integrity of the handed over property must be guaranteed by the bathhouse administration.
There are special places in the locker rooms for:
- installation of scales;
- drying hair;
- installation of a washbasin;
- foot baths;
- for staff accommodation;
All furniture must have surfaces that ensure high-quality sanitary treatment. The furniture used should be of rigid or semi-rigid models. It is allowed to use semi-synthetic or synthetic materials as upholstery for this furniture. The use of upholstered furniture is prohibited;
Similar furniture is installed in the washing department. In addition, showers and water taps are installed in the premises for the specified purpose (at the rate of 1 tap for ≤ 8 people). There are recommendations for installing additional taps used during cleaning;
Steam rooms are equipped with seats or shelves. This room is finished from the inside using materials that are safe for humans;
If linen is provided for rental, it is stored in a separate room. Moreover, clean and returned linen are stored in different rooms. If returned laundry is stored indoors for a day or more, a separate drying room is required.
In the staff room, cabinets are installed for separate storage of employees' workwear and their personal clothing.
State Fire Supervision Requirements
At the design stage, familiarize yourself with the basic requirements of the PPB. They should be taken into account both when planning premises and the alarm system in them, and when choosing sauna cladding; for example, the use of resinous wood is strictly prohibited. Deciduous trees are preferred.
The walls of the steam room are made of durable material (brick or concrete, that is, type I fire partitions are installed), the ceilings are made of type III (reinforced concrete). A separate exit from the dry heat room to the street is required (not to the reception, staircase or somewhere else).
The volume of the dry heat room is strictly standardized:
- 8-24 m3;
- with a height of -1.9 m.
An electric heater (heater) is selected based on the volume of the sauna, provided that it consumes no more than 15 kW. Permitted continuous operation is eight hours. After this, the electric heater should turn off automatically.
Additional requirements for it:
- The control is mounted in front of the steam room.
- All cables are made with the maximum degree of protection and heat resistance.
- The heater is installed at a distance of 0.2 meters from the wall to avoid fire.
- A shield with a 5-centimeter gap from the ceiling is mounted above the heater. The shield material must be fireproof and prevent overheating and destruction of the ceiling.
The maximum permissible temperature in the sauna is 110°C. The steam room is under no circumstances sealed. You need to leave a gap of 3 cm between the floor and the door. This allows for a flow of dry, hot air into the room.
The dry heat room itself (steam room) is equipped with a deluge (dry pipes connected to the water supply system are installed along the perimeter of the “steam room”). The control is installed before entering the dry heat room. Some designers propose to “close” the steam room with thermal sensors of the “sauna” type with a PTLM wire; this system is triggered at 150°C.
Showers can be classified as rooms with wet processes. They do not install AUPS. Smoke detectors must be installed in locker rooms, administrative and service rooms. In these rooms, it is prohibited to use coating materials that are easily flammable and highly smoky.
The presence of additional, more stringent requirements may be due to the large throughput of the enterprise, the presence of additional premises (billiard rooms, stores of related products, cafes).
It is unacceptable to allow persons under 18 years of age to operate sauna equipment. All workers servicing sauna equipment must be trained in safe working techniques and know the safety regulations.
They must know:
- rules for turning on/off equipment;
- main types of problems;
- their actions if any malfunctions are detected;
- their actions in the event of a fire.
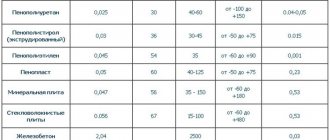
Use air heating sensors that automatically turn off the electricity supplied to the heater when overheated as a supplement to RCDs and automatic machines. Use basalt/mineral board as thermal insulation material. Treat wooden surfaces with fire retardants at least twice a year.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
Fire extinguishing systems in saunas can be manually started. The first ones are not very good due to the human factor, the second ones are prone to false alarms. To correct the situation, it is recommended to use not only smoke detectors, but also temperature detectors and flame detectors in conjunction with them.
To avoid fire in the sauna it is prohibited:
- install homemade heating elements;
- leave the heater running unattended;
- use additional heaters in the steam room;
- use electric ovens that are not equipped with thermostats;
- close the gap under the steam room door;
- dry clothes on the heater.
During the design process, check to see if there are separate safety regulations developed for saunas in your region.
equipment requirements
If you plan to equip shower cabins with special showers (needle, rain, circular), they, if possible, are installed in closed cabins.
Open showers in the washing compartments are equipped with special shelves and hooks for placing washing accessories on them, and the booths themselves are separated by a solid partition.
Enclosed showers and baths must include a changing room. Its obligatory attributes are a hanger and a small mirror. It is prohibited to operate bathtubs with damaged enamel in accordance with the provisions of current regulations. Only enamel bathtubs are allowed to be used. As a last resort, it is allowed to install bathtubs with other artificial coatings.
The faucet handles in the washing compartment and steam room must be made from heat-insulating materials.
Visitors are offered basins for washing, which must be made of materials that have high anti-corrosion resistance and immunity to the negative effects of household chemicals (cleaners, disinfectants, detergents). The number of basins is determined by the number of available seats at the rate of 2 basins per visitor.
Basins used to wash feet must be appropriately marked and different in color or shape. Basins with defects (cracks, loose handles, nicks) are prohibited from use. It is also not allowed to use wooden washers for washing.
In the washing department and locker room, bins with lids are installed to collect garbage (brooms, soap) and returned linen. With appropriate markings.
Any bathhouse is equipped with the necessary cleaning equipment. The latter is marked and used strictly differentiated: for the toilet, washing room, locker room. Inventory is stored in a special cabinet or a separate room is allocated for these purposes.
During the operation of the bathhouse, routine cleaning of the premises is carried out periodically. Upon completion of the bath, cleaning and disinfection are carried out.
General cleaning is required weekly. All surfaces of each of the bathhouse premises and the furniture installed in it are disinfected. Identified technical defects are eliminated during general cleaning.
Two types of planned treatment are carried out monthly: disinsection and, in parallel with it, deratization.
Cleaning work is carried out in accordance with the requirements of standard 51870-2002 (GOST).
Requirements for ensuring epidemic well-being
These requirements imply:
- monthly activities to exterminate rodents and parasites;
- ongoing elimination of defects in floors and walls (as cracks form);
- weekly general cleaning;
- routine cleaning during the working day;
- the final “promenade” of the cleaning employee at the end of the working day, the last cleaning is done with the mandatory use of disinfectants.
The SES will definitely check the disinfection log and the consumer’s corner in the sauna.
Personnel requirements
When applying for a job in a bathhouse, the future employee is required to undergo a medical examination and provide (get) a medical record.
In the process of work, he is obliged, according to existing schedules, to regularly undergo a medical examination with a note in his personal medical record. It must include:
- Laboratory test results;
- Information about past infectious diseases;
- Information about vaccinations received;
- About the hygienic training completed (taken once every couple of years);
History of the bathhouse
Bathhouse is a room equipped for washing the body with the simultaneous action of water and hot air or steam. Often this concept includes the entire complex of actions carried out by a person in a bathhouse or related to it.
Sauna is a Finnish word meaning an enclosed room, the interior of which is made of wood, heated by a special stove with stones. It creates a dry, hot environment that is beneficial for humans. The word “sauna” does not mean the process itself, not the functional purpose of the bath, but the structure itself, made in accordance with certain requirements: in the corner there is a brazier oven, on the grate there are stones over hot coals.
The history of the bathhouse dates back to ancient times. In Egypt, more than 6 thousand years ago, they attached great importance to the cleanliness of the body; as a rule, cleanliness and health are inseparable things, and the treatment of various diseases by their healers almost could not do without a bath. In India, too, the bathhouse was widely used for hygienic and medicinal purposes.
In Ancient Greece, baths, in the form of a round room with a stone open hearth in the center, first appeared among the Spartans. And then they spread all the way to urban - public ones.
The bathhouse was especially loved and popular among the ancient Romans. “Bath, love and joy—we are together until old age,” this inscription has survived to this day on the wall of one ancient building. In the bathhouse, the Romans not only washed themselves, but led a bohemian life. There were also rooms for massage, exercise and sports, and libraries. They even resolved important state issues. Rich Romans visited the bathhouse more than once a day.
The sweating rooms were heated in the same way as in modern Russian baths and Finnish saunas. There were also rooms with dry and wet steam. In ancient Rome, baths were valued as a remedy for many diseases.
The steam bath (soap room, movnya, mov, vlaznya) in Rus' was known among the Slavs already in the 5th-6th centuries. Everyone used the bathhouse; there were many private and public bathhouses in cities and villages. Many foreign travelers have written about Russian baths. The construction of baths was allowed to everyone who had enough land. Home baths were heated only once a week, on Saturdays, so Saturdays were considered bath days. In home baths, the whole family washed at once. Baths were placed mainly on the banks of rivers and lakes, away from residential premises, so as not to carry water from afar, and in the event of a fire, the fire could not spread to residential and outbuildings.
From the 16th to the 17th centuries. Public baths began to appear in large cities; visiting them was paid. They were quite comfortable, with warm dressing rooms and dressing rooms. Visitors were given brooms and brushes, and the services of a washer were offered.
In public (“trade”) baths, people of any age and gender also steamed together, however, women were on one side, men on the other. Since 1743, a Senate decree prohibited men from washing together with women in public baths, and men over 7 years old from entering a women’s bathhouse, and vice versa.