What does jute insulation look like?
Most often, the material looks like a voluminous roll of golden-colored tape. Its width is 15–20 cm. If you unfold the insulation, you can see a rough pile. Plant fibers can be compressed or simply combed. The most common thickness of the canvas is 0.5–1 cm.
Jute is a plant native to Asia. It is widely used in textile production: bags, ropes, insulation and much more are made.
Where is it used?
Natural insulation is widely used in the construction of houses. The material fills the inter-crown space. It is often called “inter-crown jute” (“crowns” is the traditional name for wall logs). For installation, a piece of suitable size is torn off from the tape.
Jute insulation is used for wooden structures - bathhouses, log houses and houses made of timber. It is highly effective in terms of thermal protection, does not change the properties of wood and protects it from biological destruction.
Due to the content of resinous substances, jute is resistant to moisture and has antibacterial and antifungal properties.
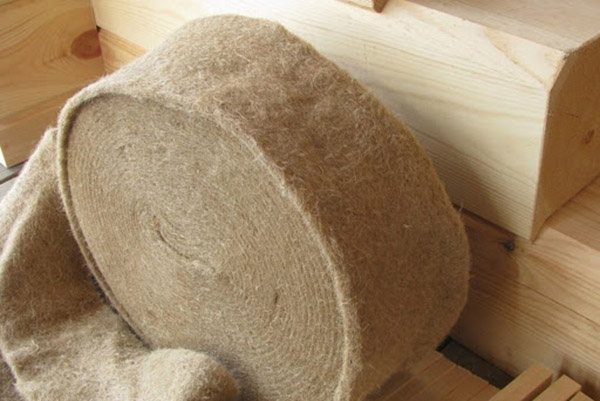

Jute as inter-crown insulation, tow and flax wool
Having worked for more than ten years in the construction of wooden houses, I can share with you invaluable experience in the construction, insulation and finishing of wooden houses from timber and logs, the correct construction of wooden log houses and caulking of houses.
Many people know the advantages of permanent living in a wooden house made of timber and rounded or simple chopped logs. These advantages over stone houses are due to the characteristics of wood. Wood is a natural super material that has only a beneficial effect on the human body and does not cause any allergic reactions. Without errors, an assembled wooden house will be much warmer and more comfortable than houses made of brick or concrete.
The main task when building a wooden house is to comply with technological requirements and compliance with building codes and regulations. Inter-crown insulation (sealant) for the walls of a wooden log or cobblestone house is of decisive importance for the thermal protection of a wooden house. The comfort of a constructed wooden house depends on the correct choice.
Inter-crown insulation must be effective in thermal protection of a wooden house, not deteriorate the properties of the tree itself, and especially not contribute to its biological destruction.
In nature, there are several main types of insulation for the walls of wooden houses made of timber and logs, differing in the quality of thermal insulation and their technical characteristics, which in themselves are quite important.
Today, the most effective are inter-crown insulation made from jute - jute non-woven fabric, flax-jute, flax batting and tow tape. Jute or jute inter-crown insulation is made from jute fiber supplied to Russia from India and Bangladesh. Linen batting is also a non-woven insulating fabric consisting of 100% flax. Flax-jute consists of 15-20 percent flax and 80-85 percent jute. The percentage may be slightly different. Tape tow also consists of 100% flax or jute and is used mainly for insulating the crown joints of log and log houses. It is also widely used for caulking houses and sealing joints between logs and joinery (windows and doors). The usual width of ribbon tow is 15 cm and thickness is 0.8-1 centimeter.
In recent years, the vast majority of construction organizations and private developers have used inter-crown insulation made of jute and flax-jute to insulate inter-log joints. Linen wool is used more often by individual developers who purchase linen wool on construction markets, being confident that what they are buying is jute (jute insulation). Here the private developer needs to be more careful, since jute insulation is usually not sold on construction markets. Under the guise of jute, unscrupulous sellers sell unknown products made from low-grade flax, including flax tow, at a “cheap” price. Jute insulation is usually sold in specialized companies that professionally deal with products made from jute (jute fabric). For finishing, it is also advisable to use decorative jute ropes.
When building your house, maybe once in your life you need to be very attentive to the choice of building materials.
Very often, novice builders ask: what is best for insulating crown joints? Linen, tow or jute?
You can answer this way. All of the listed insulation materials made from jute and flax are suitable for insulating inter-crown seams. There is no particular difference in what the interventional insulation is made from - flax or jute! The main thing is not the type of material from which it is made, but its environmental properties (naturalness) and its density! That's the main secret. This is the density of inter-crown insulation. It can be thick (more than 1 cm thick) but at the same time have low density. As a result, it will be poor insulation, even if it is made of the vaunted jute. A dense insulation with a smaller thickness will be more effective and of higher quality. This is what you should pay attention to. Here's my answer.
My other advice is to pay close attention to the team of builders who will assemble your wooden house. The quality and thermal protection of your home will largely depend on their professional skills.
If you need to insulate a room from all sides: i.e. ceiling, floor and walls; to insulate the ceiling and floor, it is best to use mineral wool insulation or “penoplex”, since it is even used for insulating houses in permafrost areas, which means it will reliably protect the room from the penetration of cold air. Consequently, it can be safely used in insulating the floors and ceilings of a wooden house.
To insulate wooden walls of wooden houses, I recommend using insulation made from jute, flax-jute and needle-punched flax with a surface density of 450 grams per 1 square meter. To insulate wooden houses chopped with an ax, tape tow made of jute and flax is suitable.
LLC "Teplye Doma" Telephone
Technical characteristics of jute insulation
Jute thermal insulation can have different technical characteristics depending on what shape it has and what fillers were used. Let's consider the properties of felt insulation, which is used most often:
- Thermal conductivity
. According to this indicator, jute is close to polystyrene foam. Its thermal conductivity is only 0.035-0.036 W/m/K. - Moisture absorption
. For jute felt this figure is within 1%. This means that it can be safely used to insulate structures where there is high humidity. - Surface density
. For the material it is on average 30 kilograms per cubic meter. - Flammability
. Jute belongs to class G4, that is, it is a highly flammable insulation material that has a smoke temperature of over 450 degrees Celsius. The material can independently support combustion for more than three hundred seconds. - Vapor permeability
. This indicator for jute insulation is about 0.3 mg/(m*h*Pa). That is, the heat insulator can almost freely pass steam outside and outside. - Soundproofing
. Jute felt can absorb sounds from low, mid and high frequencies. Belongs to the NSV-211 class. - Environmental friendliness
. The material does not emit any harmful compounds and does not attract birds, insects and rodents. It is convenient to work with it, as it does not generate dust and does not require the use of personal protective equipment. - Lifetime
. According to recent studies, the shelf life of insulation for jute beams is comparable to the durability of the wooden structure itself.
What is building moss?
Building moss for log houses remains a good solution, since this material has good thermal insulation qualities and the ability to ensure normal air exchange. This is one of the cheapest insulation materials, since it does not require special cultivation: unlike jute and flax, in Russian conditions it grows on its own in marshy soils. Which moss is best for a log house?
In the forests in the swamps of the middle zone, you can find two main types of moss, differing in their properties:
- Sphagnum , also called white moss. Most often, it chooses swampy soils and coniferous forests, forming a dense, bright green carpet on the surface of the earth. This type of moss is highly hygroscopic, so it is not used as insulation often. When used for a long time as insulation, sphagnum gradually crumbles, and its use is not very reliable.
- Cuckoo flax moss has completely different properties , which are found more in clearings, as well as on marshy soils in the forest zone. It is brown in color and in appearance partly resembles flax stalks, which is why it got its name. Unlike the usual sphagnum moss, it is more dense and does not absorb water; it feels quite dense and elastic to the touch. It was used by carpenters in Rus' as the most reliable insulation material, which even today is ahead of many artificial materials.
How to collect moss for log houses? This is handmade, which also depends on the type of moss chosen.
- It is better to harvest sphagnum in clear sunny weather, as it will be much easier to dry. It is not afraid of the bright sun and, losing moisture, does not lose its insulating properties.
- Kukushkin flax, on the contrary, is best collected on a cloudy day, as it does not like bright sun. To collect moss, it is better to choose a forested area rather than a swampy one; a lot of plant material can be collected under the trees.
In swamps, the moss will be too wet, but in the forest under the trees you can easily collect the required amount, and there will be no problems with drying later.
- The collected cuckoo flax is laid out to dry in the form of a ribbon. Subsequently, it forms a kind of tape insulation, which can be used to lay the crowns of a log house.
- Sphagnum moss is stacked like hay bales, in small bunches. This allows you to dry it without damaging the rather fragile structure.
Drying usually takes approximately 1-2 weeks depending on the moisture content of the collected material.
Advantages of jute insulation
Among all inter-crown heat insulators, jute has a number of advantages that are unique to it. Let's look at them:
- Bonding ability
. Jute contains lingin in large quantities. It is a natural resin that prevents rot and mold. In addition, it is capable of gluing fibers and timber together, making the seam airtight. - High rigidity
. This quality is responsible for the fact that jute practically does not wrinkle over time, which means it does not lose its thermal insulation characteristics. - Highly environmentally friendly
. Good quality material contains exclusively natural components, so jute cannot emit any toxic volatile compounds during operation. - Easy to install
. To lay jute in the inter-crown space, you do not need any special tools. All work can be done independently. The material does not emit dust and does not irritate the skin and mucous membranes. - Good vapor permeability
. This quality guarantees that an optimal climate will be maintained inside the building. - Versatility
. Felt jute, thanks to its good compressive resistance, can be used to insulate not only seams in wooden houses, but also floors, walls, and roofs. - Aesthetics
. The material has a golden natural color that matches perfectly with the color of natural timber or logs. Therefore, no additional decorative processing of jute is required.
Disadvantages of jute insulation
The main disadvantages of this thermal insulation material include the following:
- Relative fragility
. Since jute is a completely natural material, its service life is short. And if wood can be coated with protective compounds, then the insulation will have to be changed from time to time. - Reduced thermal insulation qualities when wet
. Although jute is difficult to wet, if it absorbs moisture, its thermal conductivity increases sharply. It takes a very long time to dry. For the same reason, it cannot be installed in wet weather. - The need for caulking
. To prevent cold air from blowing through and entering the room, the building must be additionally caulked.
Natural thermal insulation materials
Natural heat insulators include:
- moss;
- flax - represented by tow, felt and batting;
- jute in the form of felt and tow;
- jute-linen (mixed tape insulator);
- natural felt (made from sheep's wool) is a new product on the construction market.
Moss
Moss is one of the oldest insulation materials for the gaps between the logs of wooden buildings. However, working with such heat-insulating material is more difficult than with tape heat insulators. But sometimes it is irreplaceable:
- the financial capabilities of the developer are limited - the material is obtained for free, albeit with great effort;
- the house is built from hand-cut pine trunks - it is convenient to select the thickness of the insulation to match the diameter of the log;
- the owners have chronic respiratory diseases - it releases phenolic and triterpene substances into the air, which have a healing effect on sick family members.
The best option
The experience of professional builders shows that the optimal solution in terms of price/quality is a combined option - flax-jute or jute felt with admixtures of flax (sometimes other components). Jute gives the structure the necessary rigidity, and flax gives elasticity and elasticity. The ratio can be 10/90 or 50/50.
There are standards for using flax jute for different types of timber:
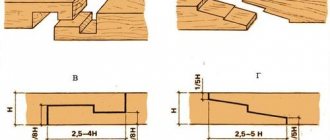
- For example, for a beam 150 by 150 mm, the width of the jute insulation should be 152 mm with a thickness of 5-8 mm;
- For chopped logs, wider felt with a width of 100-150 mm is used. In the case of a rare log house with a thickness of 250 mm and above, you can find strips of a similar width. For example, on the website of one jute manufacturer it is stated that, if necessary, you can cut ribbons up to 1600 mm wide.
How much does jute cost?
The price of flax jute depends mainly on density. The density is selected according to the project and largely depends on the weight of the structure lying on the insulation.
For example, well-known Russian jute felt is sold with a density of 250 g per m / p, thickness 2-4 mm (thin), 100 mm wide at a price of 4.5 rubles per meter, 150 mm wide at 6.5 rubles per linear meter. With a thickness of 4-6 mm, prices will increase to 5.7 and 8.55 rubles, respectively.

If the width of the strip for the log house is insufficient, the material can be laid in 2 layers. Material consumption increases and, naturally, so does the cost.
Also keep in mind that tape will be needed for insulation in the corners of window openings.
The table below shows the price depending on the volume of purchases and other types of insulation.
Application
Technique for laying inter-crown sealant on a log
Let's look at how to properly use the material in your work.

Laying moss.
Moss must be laid in the following way:
- If it is dry, then tamp it in a barrel and fill it with 20 - 30 liters of water. Leave for half an hour, drain the water, and squeeze out the moss.
Remember! Dry moss does not allow itself to be manipulated, so pre-washing will allow the material to become more pliable.
- Take ready-to-install moss.
- Lay it across the log without compacting it. Please note that the seal must lie evenly.
- Make sure that the width of the layout is 200 - 250 mm, and the thickness is 40 - 50 mm.
- Laying in the bowl is made with a thickness of 4–5 cm, and the protrusion beyond its limits is 5–10 cm.
Advice! Lift one end of the log and place it on the bowl, then lift the other end, about 50 - 60 cm higher from the place of laying, so as not to move the moss, and release it into the opposite bowl.
- Tap the entire surface with the headstock.
- Perform all subsequent actions as described in paragraphs 2 – 7.
- Take a construction stapler and secure the laid material every 30–40 cm.
Tow is less problematic to work with, since the finished canvas does not require additional time for cleaning and even laying on the log.
Tape jute is especially convenient to use.
It differs only in the installation methods:
- If the timber is for a bathhouse, profiled, glued, then we lay the insulation without bends. We don't use a stapler.
- If the log is ordinary, profiled with natural moisture, then the material must be folded once with a lock. Make sure that the canvas does not extend beyond the edge of the end.
- If the bathhouse is built from a wild log house, a fire monitor structure, or from a milled log, lay the tow in two layers. Use a stapler to secure the fabric.
Attention! Crumpling the canvas is prohibited, as this leads to poor shrinkage and further damage to the wood.
Log caulking technology
Caulking is a stage in the construction process whereby gaps and crevices are filled with a special material to prevent the inside of a room from coming into contact with the outside environment.
Kinds:
- stretch (photo);

Caulking of a stretched log house.
- set (photo).

Caulking set.
The goal of the work is to fill the visible cracks tightly, without gaps.
Progress:
- Select a specific area as the primary task.
- If the material is in a log (just insulated), push the protruding part into the gap.
- Take the caulk in one hand and insert the tool into the crack.
- After it stops falling into the gap, proceed to tapping it with a mallet.
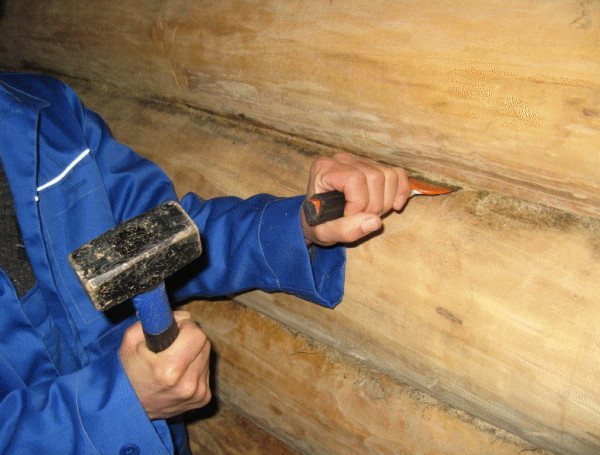

The caulking process goes like this.
- Next, compact the next section on the same log, and so on, along the entire length in a circular direction.
- After external caulking of the bath, proceed to the internal filling.
Remember! One log needs to be compacted, both on one side and on the other.

Modern caulking tool.
After 12 months the process must be repeated.
Insulation for a house made of edged timber
Linen and jute tow, batting and peat moss are used as inter-crown insulation for houses made of edged logs.
Moss is used to insulate baths and auxiliary buildings. For a residential building, flax or jute material is better suited; strips of batting or tape tow are laid between the crowns, corners and irregularities are caulked with tow. After shrinkage of the log house, additional “finishing” caulking of the seams is done from the outside and inside.
When asked which material is better, experts do not have a unanimous opinion. Jute fibers are more elastic, and linen fibers are soft and elastic; it is better to use flax as tow. When building from edged timber with roughly processed layers, it is recommended to use jute batting; for planed timber, linen insulation is recommended.
The best solution when choosing inter-crown insulation may be flax-jute batting; when constructing from three-edged timber or timber-laft, the inter-crown seams are additionally caulked with linen rope with a diameter of 20 mm.
Jute. Linen
What is jute and where can you buy it? Which jute insulation is better - pure jute or flax - jute? Why are flax fibers added to jute insulation? These are the questions you can often hear from people planning to buy jute as inter-crown insulation for building their wooden house from timber (logs)!
We answer: High quality of sealing between the crowns of seams (grooves) of wooden houses made of logs and beams is achieved through the use of a special insulating natural fabric made from bast fibers of jute, hemp and flax, using industrial needle-punched technology for manufacturing tape fabric.
Jute is an annual spinning plant from the linden family, up to three meters high, with an erect, branched stem, tap root and serrated leaves along the edges.
Jute is an industrial spinning plant that occupies one of the first places in the world in the production of natural fiber after cotton (among natural fibers).
The jute plant is grown in warm and humid climates in subtropical regions of Asia. The center of origin of jute is the territory of Bangladesh and the southeastern states of India. It is in Bangladesh that up to eighty percent of high-quality jute fiber is produced. Currently, the main world production of jute is concentrated in Bangladesh, India, China, Nepal and Thailand.
Flax fibers are fibers from the stem of the flax plant. Modern scientific studies of the composition of flax fiber have shown that the flax plant has a number of characteristics that qualify it as an indispensable insulation material for crown joints. Flax fiber is capable of accumulating and releasing moisture depending on the external humidity of the environment. Flax prevents the appearance of fungus, is not affected by moths and other microorganisms, and does not contain substances hazardous to human health.
So, by combining these two bast crops – flax and jute – under industrial production conditions, we get an excellent, very warm flax-jute inter-crown insulation.
Jute insulation for inter-crown grooves in logs is golden (yellow) in color and does not have straw impurities (bonfires). Jute insulation sometimes has a yellow-gray color. This means that in front of you is flax-jute. Flax-jute is used with greater success than pure jute in insulating wooden houses. It combines the best qualities of flax and jute. Pure jute is more suitable for mats and technical packaging fabrics.
Interventional insulation for profiled timber
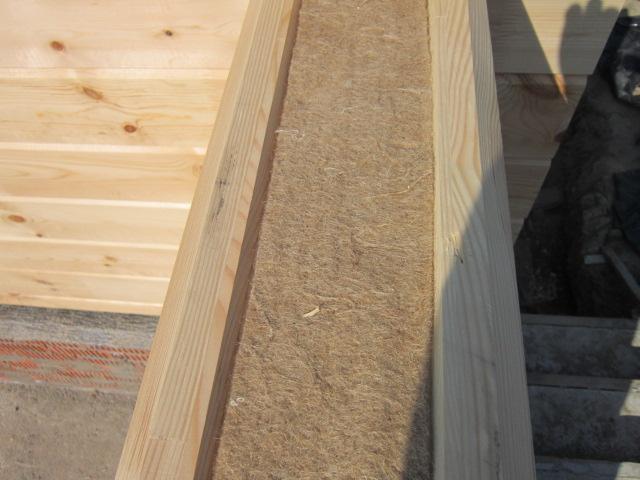

Houses made of profiled timber do not require caulking of the crown joints with tow; for insulation, a material with a tape width that follows the shape of the groove is used; in addition, this layer acts as a sealant. Manufacturers produce inter-crown insulation for the profile of any timber; the thickness and width of the material depend on the shape of the profile and the standard size of the timber. When purchasing corrugated timber for building a house, they immediately purchase a set of inter-crown insulation. Insulation is placed in the profile of blanks from house kits in industrial conditions.
Natural felt made from jute, sheep wool or “flax-jute” is used as insulation for profiled timber. After erecting a log house or assembling a house kit, to eliminate flaws, selective “finishing” caulking of the seams is carried out with flax tow.
A little more detail
Combed tow was a manufactory product and, along with marsh moss, was used for insulation - lining the walls of wooden huts of log construction. But ordinary tow has such disadvantages as the difficulty of uniform laying between the crowns and the difficulty of fastening it. Thus, ensuring a uniform density of the insulating seam between the logs in the huts was quite difficult and inconvenient. Therefore, after such material as flax , carpenters and log assemblers began to use it instead of ordinary tow.

Photo: this is what our inter-crown flax batting looks like.
By using flax wool, the assembly time of log-frame wooden structures was reduced, the quality of insulation of the inter-crown seam between the logs was improved, and most importantly, the consumption of insulating materials during the construction of wooden log houses was significantly reduced.

Photo: jute batting is comparable in its characteristics to flax batting, but contains in its composition a very insignificant presence of brome - the stems of the textile plant itself.
Do-it-yourself finishing caulk
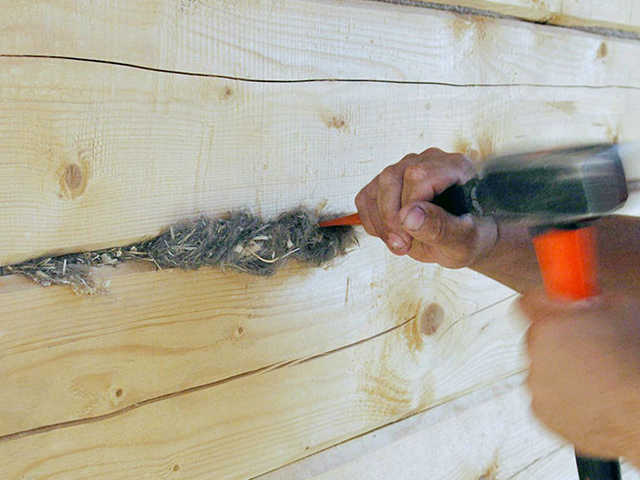

After the log house has been subjected to shrinkage, finishing caulking is carried out at home. During the shrinkage process, the previously laid layer of insulation is deformed, voids can form in the inter-crown cracks, and vertical cracks can form in the corners of the frame. The operation is performed from the outside and inside. Caulking is a labor-intensive process that requires diligence and attention; the main tool is a wide wooden chisel or rubber mallet. To avoid damaging the integrity of the fibers, it is better to blunt the chisel. The operation begins with the lower crown along the entire perimeter, after caulking of the first crown is completed, they move on to the second, etc.
"Ancient" methods of insulation
You can also use simpler and long-used options. For example, use moss as insulation. Many species of this plant grow in nature, but only two varieties are best suited for insulating a wooden house:
- sphagnum - has a large amount of antiseptic substances. This feature allows you to reliably protect your home from the harmful effects of the environment;
- Kukushkin flax has less antiseptic effect. This moss is not laid completely dry, so its thermal insulation properties will be better.
Such insulation will help create a better microclimate in your home. This is created due to the aroma of the forest that the material emits. There will always be a pleasant atmosphere in your home.
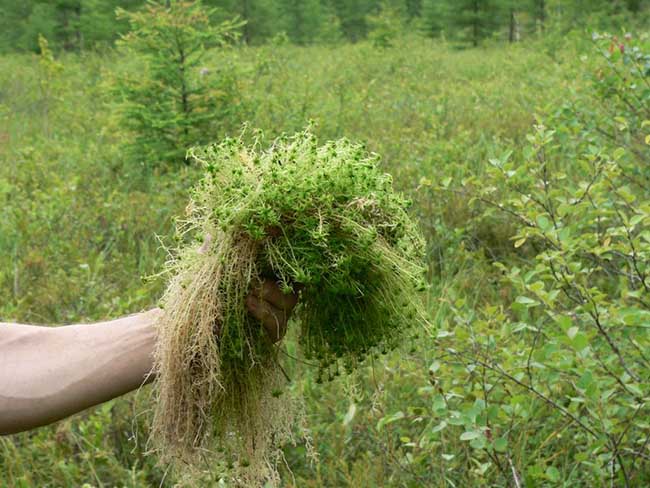

Ordinary moss - sphagnum - can be used as inter-crown insulation.
The moss itself is environmentally friendly and does not cause allergies. But assembling it yourself is quite difficult. Moss grows in swamps and other damp places. In addition, each variety requires its own technology for collection and preparation for use. It is quite difficult to prepare it in the required quantities yourself, so this method of insulating the inter-crown space is rarely used today.
For your home, you can choose a simple tow. This material is made from various raw materials, it can be flax or hemp. But such insulation has one “bad” property: birds really like it. The fibers are easily separated from the main mass, which forces the seams to be repaired annually. In addition, tow absorbs moisture well and can rot.
Which natural insulation material should you prefer?
In order to determine which moss or tow is better for a bathhouse, it is necessary to consider and compare the characteristics of the representatives.
The advantages of moss are obvious: it does not rot, it is available and its price is low, however, the big disadvantage is that it dries out and subsequently begins to blow out of the cracks, so in areas where strong winds are normal, you will have to constantly caulk it.
When laying a log house, moss takes a lot of effort and a lot of time. Other modern materials make it possible to complete this work in a shorter period of time, so focus on the financial indicator and the allotted time spent on work.
Note! If the log house is built from wood that has been chopped with an axe, moss cannot be used. Give preference to jute or linen tow.
It must be remembered that some types of tow made from flax absorb moisture abundantly, which over time causes rotting.
However, they do have a common drawback - they are a favorite food for rodents and flying creatures (moths, birds), but moss is still less interesting for them.
Artificial materials
When answering the question - how to choose inter-crown insulation for timber, you cannot ignore artificial materials. Today this option is the most popular. One of these materials is called “holofiber”.
This insulation is made from polyester fibers using the non-woven method. The material is produced in rolls and plates, each type has its own density.
Holofiber has high elasticity. This feature is very convenient for thermal insulation of crown joints, especially when using laminated veneer lumber or non-profiled timber.
This material has no pores, which means it can warp when drying. If insulation made from natural material is used, then the appearance of cracks is inevitable. When using holofiber, additional sealing of the crown joints after the timber has dried is not required. The fibers of this material will fill the cracks that appear on their own.

Holofiber does not absorb water and retains its thermal insulation properties
In addition to a high degree of elasticity, holofiber has a number of other advantages. Experts include the following among the most significant of them:
- has low water absorption rates, less than one percent. This means that holofiber will not absorb moisture and will retain its thermal insulation properties longer even in a humid climate;
- the material does not burn even at high temperatures. This property is very important for thermal insulation of wooden buildings;
- Insects “don’t like” the material; they definitely won’t live here. In addition, holofiber is not afraid of mold;
- not only has high thermal insulation properties, but is also an excellent sound insulator;
- Holofiber has a long service life, and even over time does not require additional caulking.
You should not think that holofiber can have a detrimental effect on human health. This material does not cause allergies, does not emit harmful substances and is absolutely environmentally friendly. There can only be one drawback. If wood that was too damp was used during construction, it may be prohibited. Holofiber does not allow the walls of the house to “breathe”.
Another common inter-crown insulation for wooden houses made of profiled or laminated timber is “shelter”. This material is made from polyester fiber. Just like holofiber, it has high elasticity, which allows you to fill all the cracks newly formed as a result of shrinkage of the house. Shelter does not rot, does not absorb moisture and retains heat perfectly.
There are also more modern materials, for example, “polytherm”. At its core, it is a type of holofiber, but with greater elasticity. According to the manufacturers, the material can last 50 years. But polytherm appeared not so long ago, only about ten years ago, so it is not possible to test this in practice.
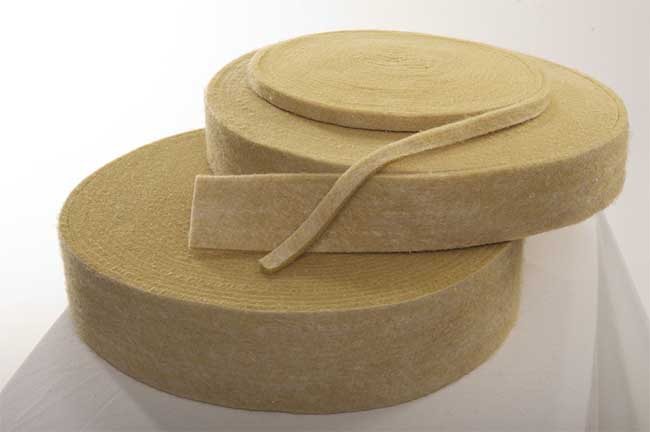

Inter-crown insulation “Polytherm” can last up to 50 years
What to put between the crowns?

To create a gasket between the crowns of a log house, there are many insulating materials. But not all of them are ideal for these purposes. First, you need to safely cross out synthetic and artificial materials from the list of candidates for inter-crown insulation. They will cope with the thermal insulation task well, but the price of their work will be damaged crowns of the log house. Artificial materials allow air to pass through well only when they are in a fluffy form, and when they are compressed by logs, they cannot do this, which will negatively affect the wood; it may begin to rot.

There is another drawback to these insulation materials - they are made from non-ecological components. And it seems to me that many people choose wood for construction in order to be closer to everything that is clean, safe and natural. The use of artificial, synthetic insulation will disrupt the entire beneficial microclimate of the room. It is for these reasons that I do not recommend focusing your attention on these insulating materials.

And it is advisable to lay insulation between the crowns from natural materials, which consist of fibers of natural plants. They also have good thermal insulation characteristics, but they are in perfect harmony with the wood and do not cause any harm to it. Among such materials are:
Many builders cannot make the final choice of insulation, deciding which of these three materials is better.

Moss can safely be called the best insulation material. Even with the advent and development of technology, they have not yet been able to invent and create insulation that is superior to moss, unless they came close to its characteristics by producing jute insulation. There are more than a hundred varieties of moss, but only brown and white moss have shown excellent results in construction. They practically do not differ in their properties, they only have differences in appearance. White moss consists of small light green fibers. It does not have a root system, despite this it grows well. White moss produces a very valuable product - peat. Brown moss consists of longer and tougher fibers that are greenish on top and brown on the bottom. Its stems resemble flax in appearance, which is why its second name is cuckoo flax.

Both brown and white moss have bactericidal properties; they themselves are resistant to mold, fungi, and insects and protect the crown grooves from them. They allow air to pass through well, allowing the crowns to breathe. They absorb all excess moisture, leaving the wood dry, and when there is insufficient air humidity, they gradually release it, i.e. regulate the level of humidity and microclimate in the room as a whole.