Home / Insulation / Installation, repair, maintenance / How to insulate an attic ceiling from the inside?
Since the attic is an attic space adapted for living, the construction of a heat-insulating layer here will not be done quite the same as in the case of conventional floors. For the most part, it is not possible to carry out all the work from the outside, therefore, insulation of the attic ceiling is most often done from inside the room.
General recommendations
It is important to remember that we will install the insulation on inclined surfaces, this increases the complexity of the work. The thermal barrier in the attic space is practically absent due to the special configuration of the frame . The covering of the roof structure is made of relatively lightweight materials that have good waterproofing properties, but also considerable thermal conductivity.
The gables and valley should also be insulated, or our efforts will go to waste; heat will simply be lost through these surfaces. It is necessary that the thermal insulation layer completely covers all surfaces and that no gaps or untreated areas are allowed. It is important to protect the thermal insulation layer from condensation, that is, all work must be carried out taking this point into account. The roof covering must provide wind protection.
You should also pay attention to the fact that if the dimensions of the insulation are larger than the width of the rafters, then you will have to add an additional beam , having previously treated this material with an antiseptic agent, this will ensure the attic is insulated with a high-quality base!

Be sure to pay attention to vapor barrier!
Used insulation materials and calculation of the thermal insulation layer
In order for an insulation system to be sufficiently effective and not become a waste of money or, worse, do more harm than good, it must meet certain requirements. And the main one is that the thickness of the thermal insulation is selected in such a way that the total heat transfer resistance of a particular building structure corresponds to the standardized parameters established by SNiP for a specific region (taking into account its climatic characteristics).

Of course, this can only be achieved by using materials with markedly low thermal conductivity. But at the same time, it is necessary not to forget about other criteria - the comprehensive safety of using the insulation, its ability to withstand specific bath conditions (high temperatures and humidity).
Calculation of a thermal insulation system is a rather complex undertaking, which is usually carried out by appropriate specialists. However, without claiming absolute accuracy, we will take the liberty of offering the reader a calculation algorithm that takes into account all the basic existing requirements. It will be presented in the form of a universal calculator that allows you to determine the thickness of insulation for both the bathhouse roof slopes and the attic floor. But before moving directly to the calculations, it is necessary to give some explanations.
One of the first points in the calculator will ask you to indicate the planned insulation material. We will not dwell on each of them in detail - a whole array of articles on our portal is devoted to this, but each one still deserves a few words.
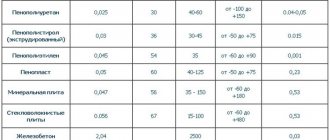
- Mineral wool is presented in the calculator in two varieties: based on glass and basalt fibers.
Both of these types have approximately the same thermal insulation characteristics - their thermal conductivity coefficient, depending on operating conditions, lies in the range from 0.038 to 0.045 W/m×°C, which is a very good indicator. Glass wool is somewhat cheaper in cost, but perhaps this is the only advantage. For roof insulation, and even more so for bathhouses, the best option would still be the basalt variety.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a birch broom for a bath

The initial characteristics are very similar, but it is still better to give preference to basalt mineral wool (right)
Basalt wool fibers are less brittle, and this makes working with it much easier. In addition, this same quality makes the material more durable - it has a much less pronounced tendency to gradual caking and compaction, with loss of thermal insulation qualities. Another advantage is that basalt wool usually has less pronounced hygroscopicity, that is, it is not so saturated with moisture.
Both cotton wool contains synthetic binders that can release harmful fumes into the air, especially at elevated temperatures. Technologists from leading manufacturing companies have managed to reduce such emissions to a minimum, and the most “clean” materials should be selected for the bathhouse - usually the packaging indicates approval for use in residential premises, and even in children's or medical institutions.
The most important advantage of mineral wool is its non-flammability, ability to withstand fire and not emit hazardous combustion products.
In a word, all this gives reason to consider high-quality mineral wool (preferably basalt) as one of the best options in a bathhouse.
- Next on the list of insulation materials is ecowool. This is a relatively new and not yet widely known material, which is a product of processing natural cellulose.
It would seem that cellulose is both a fire hazard and a tendency to gradual biological decomposition. However, in the case of ecowool, everything is exactly the opposite. Special processing of fluffed fibers and the presence of boric acid and sodium tetraborate (borax) in the material composition radically change its properties.
Ecowool not only does not decompose on its own, but also becomes a powerful antiseptic that has a beneficial effect on the wooden structural elements surrounding it. Rodents and insects do not welcome it; mold or mildew will never spread in it. And borax is an effective fire retardant - cotton wool does not ignite even when exposed to open flame.
basalt wool

Ecowool can be used to fill cavities or cover walls and partitions.
Ecowool can be installed in the cavities of insulated structures using a “dry” method, but in this case it is more susceptible to gradual shrinkage. Another method of application is to apply it to surfaces using “wet” technology, using special equipment. With this installation, thermal insulation becomes more durable and effective, but it will be impossible to perform such an operation on your own, without experience and without the appropriate equipment.
- The next item is polyurethane foam. It can rightly be called one of the most effective insulation options. Possessing excellent adhesion, it will create a durable porous thermal insulation “coat” on any surface - horizontal, vertical or even with a negative angle of inclination - such as on the back side of a roof slope. In this case, the thermal conductivity coefficient can be only about 0.030 W/m×°C.
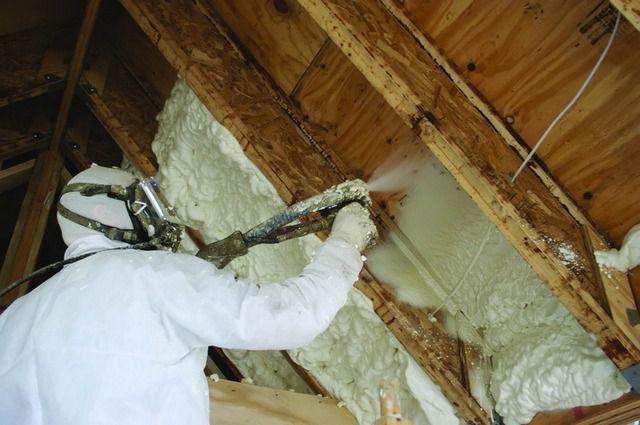

The widespread use of this insulation method is probably only hindered by the need for special equipment, which means that you will have to resort to the rather expensive services of specialists. Disposable kits for self-application of the material have also appeared on sale - with all the necessary components and accessories. However, their cost cannot yet be called affordable either.
- Insulation based on polystyrene.
This includes the widespread and very inexpensive polystyrene foam, as well as a more advanced variety - extruded polystyrene foam (a typical representative is the popular "penoplex"). These materials themselves are very good thermal insulators, but they can be used to insulate a bathhouse with some caution.
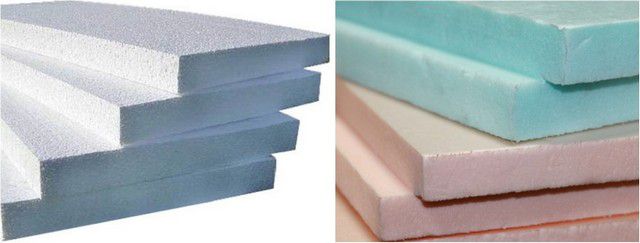
Polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam are not the best option for insulating a bathhouse
Firstly, the materials do not have thermal resistance - temperatures in the region of only 80°C are already beginning to have a destructive effect on them. Polystyrenes are unstable compounds, and the process of depolymerization cannot be ruled out, with the release of gases that are very dangerous for humans, and this phenomenon increases with increasing temperature.
Thus, there should be no talk of using it inside bath rooms at all. Secondly, the material becomes extremely dangerous in the event of a fire - it is capable of burning, spreading a “liquid” flame when melted, and the smoke released during this process is deadly. For these two reasons, in many countries, polystyrene foam is legally prohibited in any residential construction.
In the context of our publication, polystyrene foam (preferably extruded) can be considered only for insulating the roof slopes above the bathhouse, if it is not possible to use another material.
- Next - bulk mineral insulation. We include expanded clay and vermiculite in this category.
Both of these materials are more often used for insulating horizontal structures, that is, attic floors. Quite rarely, but still sometimes they are used to create a thermal insulation layer on roof slopes with a small angle of steepness.

The main advantage of bulk mineral insulation, expanded clay and vermiculite is environmental friendliness and complete safety in operation.
The natural mineral structure and the absence of any “chemistry” makes these insulation materials absolutely “clean” from an environmental point of view, non-flammable, not subject to decomposition or rotting. There will never be nests of insects or rodents in them.
Expanded clay is cheaper, but its insulation qualities are still significantly lower than those of most common insulation materials mentioned above. That is, to create effective thermal insulation, you will need a fairly thick layer of material.
Vermiculite has thermal conductivity comparable, for example, to mineral wool materials. Another advantage is its ability to absorb moisture from the air and release it with the same ease - thus, it serves as a kind of “regulator” of humidity, maintaining an optimal regime. The only disadvantage of vermiculite is its high price - not everyone can afford to create a full-fledged thermal insulation structure based on it.
- Finally, natural organic materials are traditionally used to insulate attic floors. For these purposes, sawdust, shavings, dry pine needles, and some types of peat moss have long been used.

Sawdust can simply be poured into the cavity (for example, between floor beams), but this material can cake over time, losing thickness and, accordingly, in insulating qualities. Of course, special treatment is necessary that will prevent the processes of decay of organic matter or the appearance of fungal infections, nests of insects or rodents in it. Most often, they do not just dry backfill, but mix the material with a binder - this role can be clay or cement.
Materials for ceiling insulation
To insulate the ceiling in the attic, you must first determine what materials exist for this work.
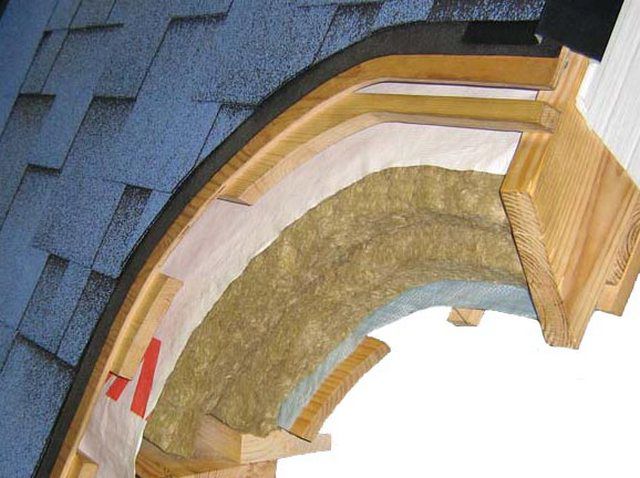
- Mineral wool is a convenient, practical, not very expensive material that is suitable for all properties. Mineral wool slabs will be easy and not difficult to install. It is compressed a little and placed in its specific section between the rafters, it is leveled and sits firmly in its place. It has high strength, does not burn, does not absorb moisture and practically does not conduct heat.
- Glass wool is a durable, effective material with high sound insulation properties and also withstands low temperatures.
- Expanded polystyrene is laid on top of the entire rafter structure; it is not suitable for insulation from the inside.
- Polyurethane foam is easily applied by spraying to any surface, thus eliminating the formation of gaps and cracks. When using this material, there is no need for vapor barrier.
- Polyurethane foam is easily applied by spraying to any surface, thus eliminating the formation of gaps and cracks. When using this material, there is no need for vapor barrier.
- Polystyrene foam is a cheap and popular material that is easy to cut and easy to install. However, it has little ability to conduct steam, which can mean dampness in the room. It is also important to remember that it is attractive to rodents.
A material such as ecowool is also used; it is applied by spraying onto any surface and is very good in its properties. The antiseptic contained in its composition does not allow the insulating layer to deteriorate, and this material also creates a dense layer.
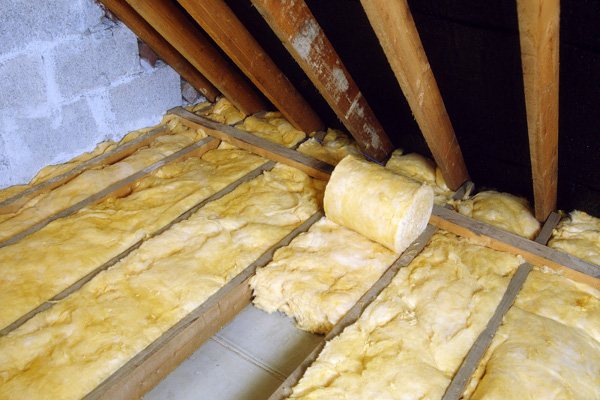

The thickness of the insulation is an important point, contact SNiPs!
There are foil materials that work both as insulation and as a heat reflector.
A gap of several millimeters is left between this layer and the vapor barrier layer for this reflective effect to fully work.
Features of the attic of the bathhouse and the attic of the house
The arrangement of the attic rooms of houses is, in principle, no different from the rooms on the second floor in the bathhouse. Only in the bathhouse there is one thing... It is hot and humid here, therefore, in order to avoid this heat and moisture from reaching the second floor, it is necessary to make good steam and waterproofing of the ceiling of the bathhouse itself. If the attic rest room is humid and stuffy, there can be no talk of any comfortable conditions for relaxation. The interfloor covering must be done correctly. It is important. In a simple residential building, you should not pay so much attention to the interfloor ceiling.
For the same reason (comfort, practicality), it is imperative to make a hatch that can be quickly closed at any time. The staircase to the second floor is not too steep and wide enough. You need to climb it easily and naturally, because after a hot steam room, you don’t really want to run up and down.
It is definitely recommended that all wooden structures, and these are rafters, attic frames, rafter beams, and floors, be well impregnated with fire protection. This treatment will significantly increase the service life of the roof, and the bathhouse in general, and will also protect against accidental fire.
Stages of work
To begin with, a layer of waterproofing is laid along the rafters, from the bottom to the ridge of the roof. It is important to know that it is necessary to leave some distance between this layer and the roof to form an air gap in order for high-quality ventilation to occur. This way you can avoid roof rotting.
Vapor barrier rolls or slabs are mounted to the waterproofing layer. If the layers of insulator slabs are thinner than the thickness of the rafters, then it is necessary to lay the slabs in two layers. If it’s the other way around, then nail slats to the rafters or beams. There should be no differences in height. A vapor barrier layer is placed on top of the insulation layer, since this layer will protect the insulation from condensation.
Typically, glassine, roofing felt, any foil materials and plastic film are used for this. This layer is hemmed and reinforced with slats. The slats are fixed in increments of thirty centimeters, perpendicular to the beams.
The vapor barrier material is overlapped, and the joints are sealed, usually with tape. After all this work, you can do the final finishing of the ceiling surface using sheets of plasterboard or other materials.
All work must be carried out carefully and in accordance with the insulation requirements. You cannot leave cracks and gaps if you do not want the work done to be in vain. It is also worth doing work on insulating walls, gables and not forgetting about the valley, since heat will be lost through these surfaces. It is important to take a responsible approach to protecting the premises from heat loss in order to be able to fully exploit the attic space.